Waterfall Model In Manual Testing: The waterfall model is a popular software development process that defines the technical approach and implementation method for developing and maintaining complex software systems.
The model, which consists of sequential phases (or stages), has been criticized as being too rigid due to its linear structure, inflexible documentation requirements, lack of mechanisms supporting change management, and, in general, as it does not take into account the inevitable changes that occur during software development due to a variety of factors.
The Waterfall Model is not a model but rather a “methodology”. While the methodologies for software development are well documented, they differ depending on their target audience and the business domain being addressed.
Definition of ‘Waterfall Model’
A waterfall model is a traditional approach to system development that starts with collecting requirements and then moves sequentially through the development process. Each phase requires the previous phase to be complete, as there should be no overlap of phases.
Every stage has input from its predecessor, so each stage relies on the accuracy of its preceding one. It is a “closed-loop” system; little can be changed once it starts.
Waterfall Model In Software Engineering
At its core, the model does discuss some very important points that should be addressed when developing a complex software system:
- The Waterfall Model defines all aspects of the development process and documents each stage to ensure no inconsistencies between phases.
- Defines a specific software development life cycle with clearly defined phases.
- The Waterfall Model is well suited for stable environments where requirements and scope are agreed upon before coding begins.
- The business expectations need to be managed, as they directly relate to the risk and uncertainty associated with the project. The delivery of the software product is also directly affected by business expectations. The Waterfall Model provides a clear path and delivery mechanism to its stakeholders.
- The Waterfall Model clearly states that you cannot return to a previous phase once in a phase (it cannot be redone). This can cause problems when many defects are found late in the testing phase, and time to fix them may not be available.
- Provides a clear deliverable at the end of each phase.
Waterfall Model SDLC
The waterfall model is often misunderstood as a sequential development process based on strict adherence to a fixed set of steps. In reality, it is much more fluid than that and provides many options for asynchronous processes, parallel development, and deferred steps. It is very much a process for managing project risk, which means it needs to allow flexibility to respond to changes.
Waterfall Model For Software Development
The waterfall model was originally developed by Winston W. Royce in 1970 for use in developing computer hardware systems, although it wasn’t called a ‘waterfall model’ until 1975 by Barry Boehm.
The waterfall model is more of a method than a model because it doesn’t specify any precise steps for software development. Instead, each step within the overall process must be defined in detail.
For this reason, the Waterfall Model can vary dramatically depending on the type of software to be developed, the size of the team, and what’s specified in the project’s documentation.
However, it follows an overall pattern that can be modified but not deviated from too much as it is still a sequential process. For this reason, it is sometimes referred to as a step-wise model since all processes are followed step-by-step, but it’s not a well-defined process.
One of the reasons why the Waterfall Model has become so popular is that software development projects can be broken down into manageable chunks of work called processes.
Each process can be assigned to a team or group of people with specific skills and knowledge to undertake the task. This ensures that the different elements of a software development project are developed logically so nothing is missed and the result is successful.
The Waterfall model consists of numerous phases or stages, each dependent on the previous phase being completed successfully before moving on to the next stage.
If any obstacles arise during development that cause major delays, it can be not easy to catch up. In addition, if any major changes are required, the model must be updated and all subsequent phases re-worked. This is why the Waterfall Model has been criticized for being inflexible in its approach and potentially leading to wasted time and money.
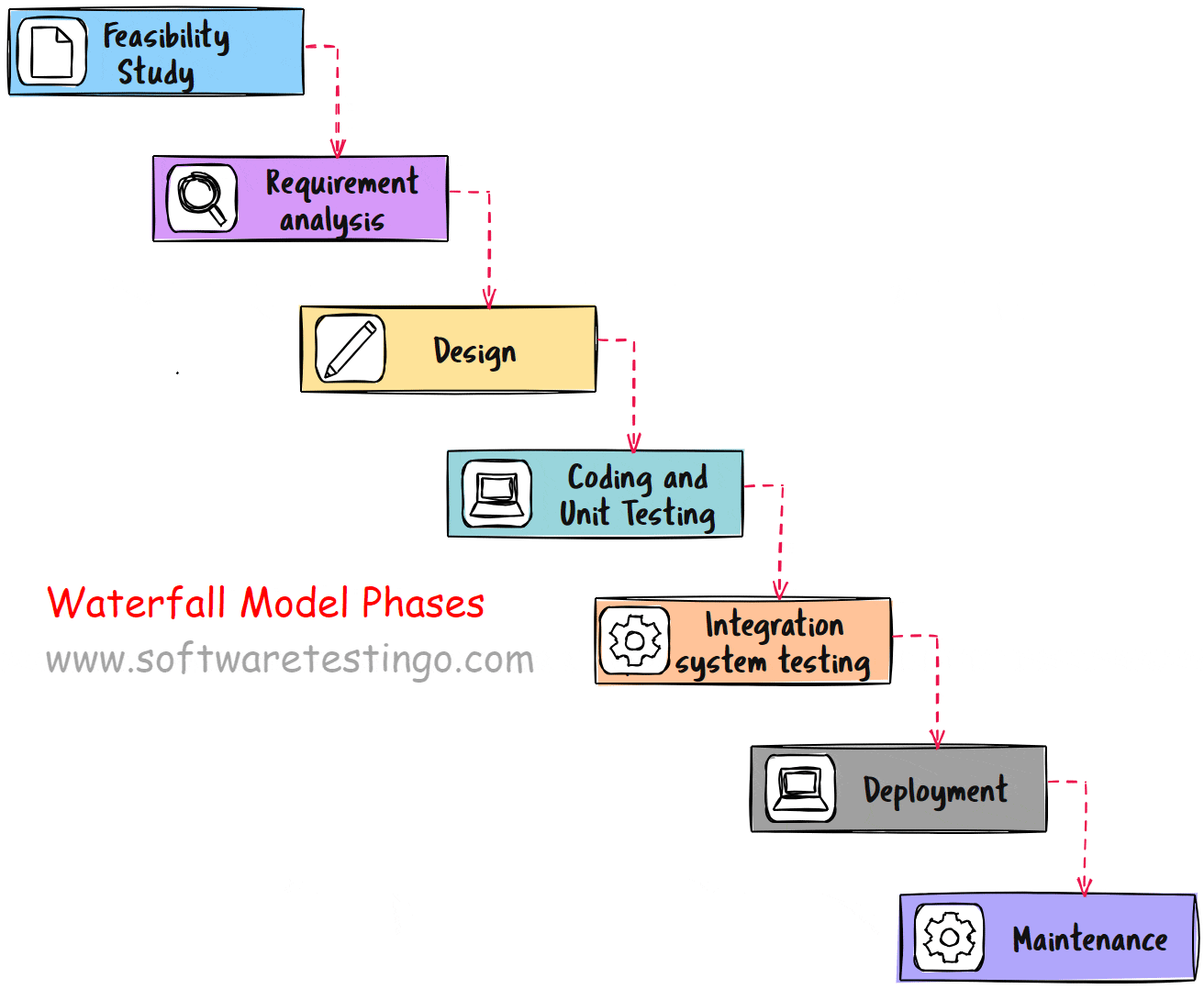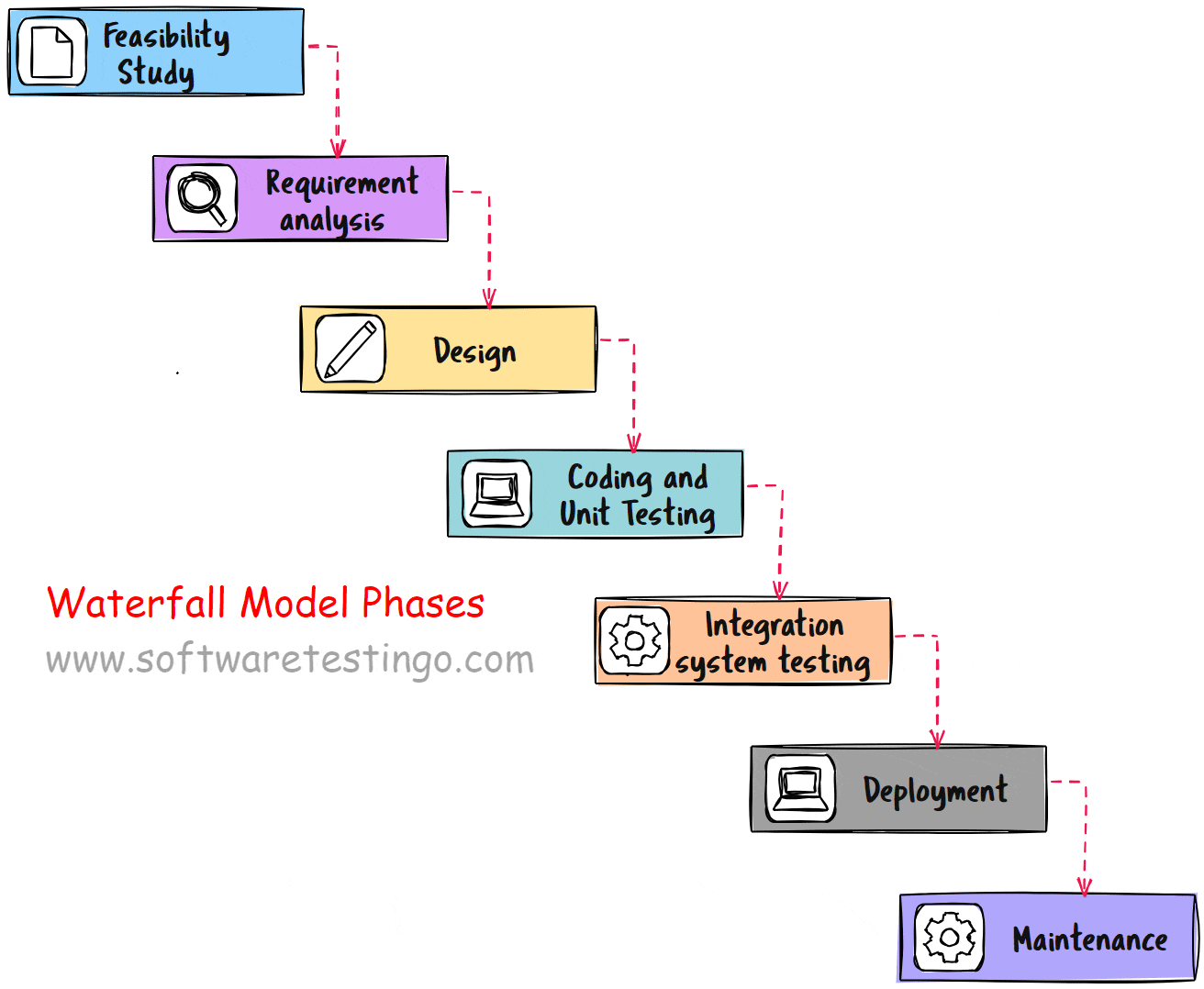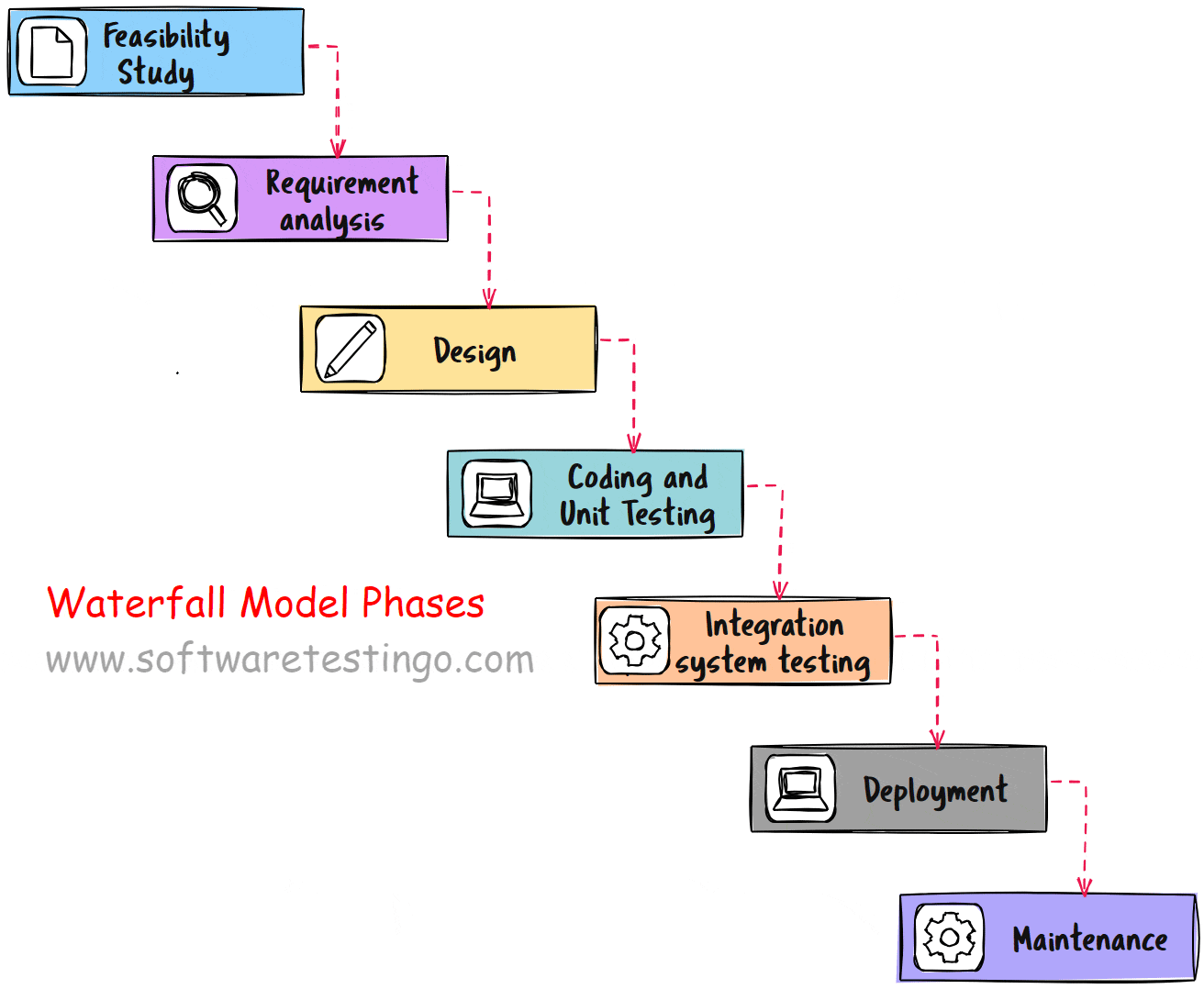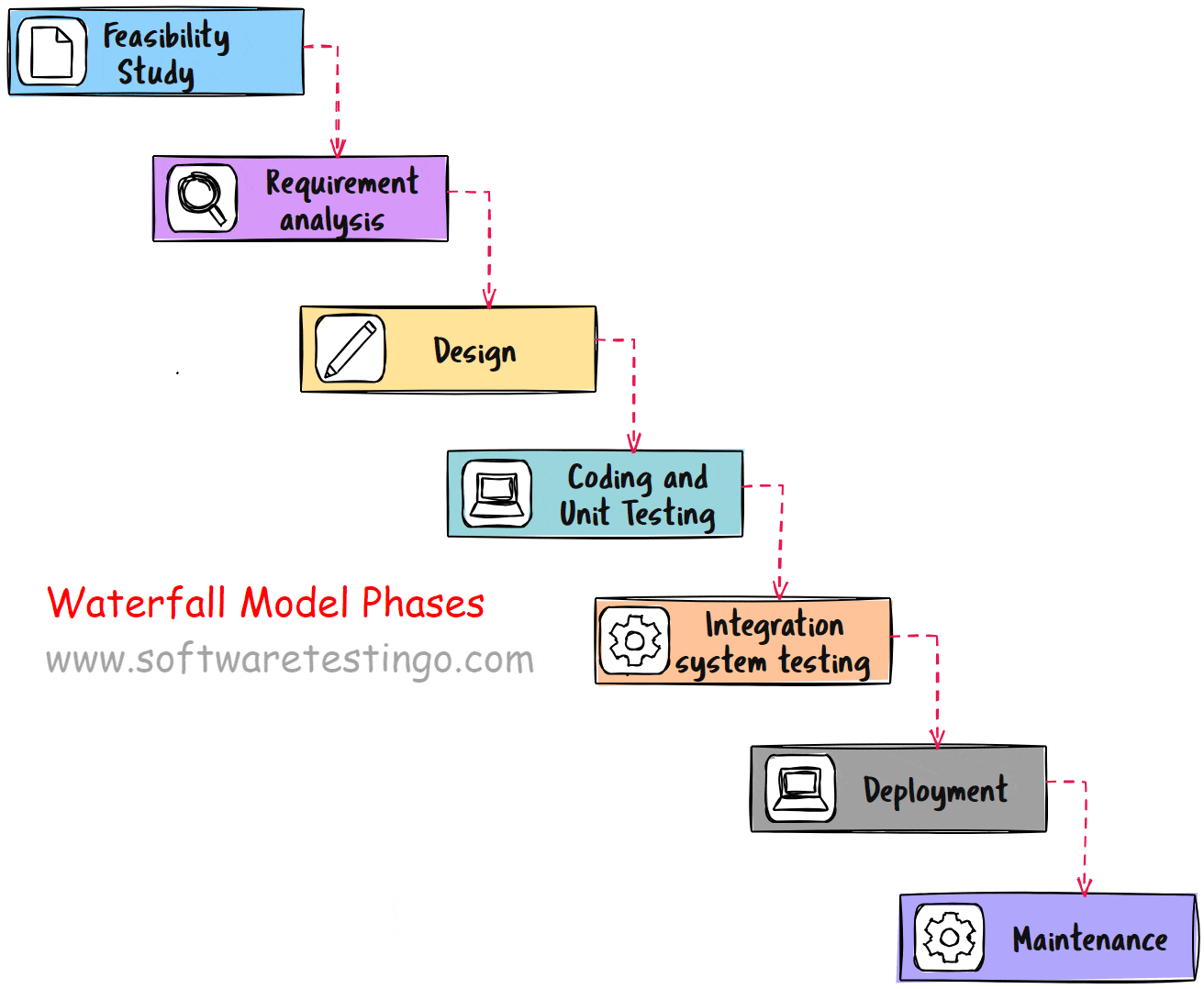
Waterfall Model Phases
Throughout the Waterfall Model phases, a series of processes must be followed for everyone to work together effectively and efficiently. There is an overlap between some of these processes necessary for team members to communicate effectively so they are not isolated from one another.
Waterfall Model Processes:
An extensive amount of planning must be carried out before work can begin on each stage, and this may take some time; it is probably the most important phase in the whole model to get right, as any problems encountered during this process could trigger a lot of time, effort and money to be wasted if not taken into account.
The requirements for each stage must be detailed so everyone knows what they are expected to achieve and how the final product should work when completed. In addition, any changes or improvements will need to go through this phase again, which may cause delays throughout the overall development process.
Significant time is spent communicating and coordinating work between team members, as many processes must be undertaken simultaneously.
Let’s Discuss each of the SDLC Waterfall model phases in detail:
Feasibility Study
A feasibility study is an investigation that assesses a project’s issues, risks, and costs. It’s usually undertaken before any implementation takes place to determine whether it would be possible to continue with the given project.
The main purpose of a feasibility study is to discover why a project needs to take place and the potential outcome. Therefore, The feasibility study aims to determine whether the project is technically and financially viable so that it can go ahead if it is.
This stage of the Waterfall Model involves different activities, such as:
- Gathering information about the requirements for a specific project or product; – Establishing and understanding what will be required to carry out the project and whether any potential problems or issues may arise along the way;
- Determining how much time, money, and other resources will be needed to successfully implement a given project if it were to go ahead;
- Establishing what is required of different team members throughout a development process.
Requirement Analysis
The requirements should be gathered and documented before any development in the next phase of the Waterfall Model takes place. The goal is to understand what will be required to implement a project – including who needs it, what features it must have, and how the end product will work.
During this stage of the Waterfall model, the team will also determine which requirements are feasible and which will be discarded.
Once all of this has been done, the next step is to document the information gathered in a requirement document that everyone can refer to when carrying out work for each stage.
Determining how a product or service should run is crucial. When requirements have been gathered, the team will need to go through them and determine whether they are reasonable within the given constraints of time, budget, and other resources.
If it’s found that a requirement cannot be implemented due to one or more of these factors, then it should be discarded as it is not feasible and is, therefore, unnecessary from the start.
Design
The design phase aims to create a detailed plan of how a product or service should run once implemented. The key aim of this stage is to determine how work will be carried out and what the outcome should look like.
To ensure that each team member is working towards an overall common goal, the design stage should include a design document that records how a project will be carried out from start to finish.
This ensures that team members will have clear direction and can refer back to this plan to see what they are expected to achieve during each stage of development.
It’s important for everyone involved in a project to be aware of what is required to achieve the end goal.
This way, team members will know where they stand and how to complete their tasks in a way that fits with the designs and implementation of others.
Coding And Unit Testing
The coding stage refers to creating code for a particular project or product. This is where the different project parts designed in the previous stage will be brought together to create something useful.
The aim during this phase is for the team members to go through and implement the design documentation that was created at the beginning of development so that what has been planned can become a reality.
If everything goes according to plan during the development process, it should be relatively straightforward for the team to make changes within a given project.
If this is not the case and some problems arise from the design stage, which has not been anticipated or planned, it could become difficult to implement or adapt features according to how they should operate. This is why it’s important to go through each stage and ensure that everyone understands their role in a project so that they are clear on what work will be required from them during this stage of the Waterfall Model.
After that, they do unit testing to verify whether each model works as expected.
Integration And System Testing
The integration stage is the next step once coding has been completed. It involves putting everything developed in the previous two stages together to function as one.
In this stage, team members should send their code to others within their given team working on different aspects of a project so that all of them can check whether their code is compatible with the rest of the team.
If all goes according to plan during this stage, then every aspect should work together as a whole, and each section within what was designed during the design stage will be fully functional.
Once this has been verified, it will be relatively easy for developers to create patches where necessary and implement new features or adapt existing ones.
System testing is the next step after development, and it involves putting a finished product through its paces to check whether it works as expected.
For this stage, all team members must be familiar with what has been developed within other sections to test them together rather than in isolation. This will make it easier to ensure that individual components fit together and work as a whole.
If any bugs or problems are found at this point, they can be fixed before the product is completed and sent out to customers or clients so that they can start using it. If there are serious issues with what has been created, the project could be put on hold so that it can be fixed and development can continue in time for release.
Deployment
This is the final stage of the Waterfall Model, and it aims to take a fully functioning product or project created through coding, integration, and system testing and get it ready for launch.
If developers have taken advantage of everything that can be done during this stage, they should be able to test how well a product or service works and get it ready for release.
Once they have done this, deployment is just a matter of getting the finished product out there so that users can use what has been created. This will show whether development has been successful and indicate how much time has passed from the beginning of development until a completed product is released.
Suppose everything goes according to plan during this part of the Waterfall Model. In that case, deployment will be relatively straightforward, and the time it takes for a project to reach this stage should be relatively short compared to other models such as Agile.
However, if some problems or issues arise during the previous three stages, then deployment could be delayed until they have been fixed, and this will slow down how quickly a project can be completed.
Maintenance
Once customers or clients have deployed and used a project, further development must continue at a much lower level.
There will likely be fixes for bugs or problems in the software so they can be dealt with quickly. Furthermore, new features and additions may be required over time to meet the changing needs of customers and clients so that they can get more out of their products or services.
It’s common for projects to enter maintenance through checkpoints, but this shouldn’t cause too many problems if they’re recognized quickly and dealt with properly.
If these issues are resolved properly, then it’s likely that further growth can be achieved through this maintenance cycle. However, if they aren’t dealt with quickly enough, it could harm the project’s future and reduce customer satisfaction.
Pros & Cons of the Waterfall Model
Next, we will discuss the Pros and cons of the Waterfall Model, as there are many discussions on both sides. It will help you understand why some developers still use the Waterfall Model for building their projects.
| Pros of the Waterfall Model | Cons of Waterfall Model |
|---|---|
| Ensures quality work through systematic testing | Difficulty in determining project costs from the beginning |
| The completed product is fully functional and ready for deployment | Uncertainty about project costs and client preparedness |
| Facilitates quick market entry in saturated markets | Challenges in estimating project completion timelines |
Furthermore, if issues with the previous stages arise later in development or testing, it could delay deployment significantly because these problems would have to be resolved before any work could continue. If these issues are not resolved quickly enough, any future growth a project or business may want to achieve could be harmed.
Waterfall Model vs Agile
Next, we’ll talk about the differences between Waterfall and Agile.
| Agile Model | Waterfall Model |
|---|---|
| More flexible implementation and project execution | It involves many stages of testing; after each stage |
| Shorter duration, allowing for quicker changes | Longer duration, providing more time for thorough checking |
| Continuous testing reduces the risk of missing functionalities | Thoroughness in checking leads to better overall product quality |
| Greater flexibility in implementing changes throughout development | Testing occurs throughout the project with ongoing deliverables |
| Lower overall project cost due to investment spread over iterations | Costs can be relatively similar, often more expensive overall |
| Affordability for developers and clients due to gradual investment | High upfront costs in Waterfall pose a financial risk |
| Challenges in estimating overall project cost due to fewer stages | More time for aspects to be checked, contributing to better quality |
| Reliance on effective continuous testing | It is Riskier for developers and clients due to limited flexibility |
Conclusion:
This blog post was all about the waterfall model, a popular software development process used to define the technical approach and implementation method for developing and maintaining complex software systems. We hope you’ve learned something new today by reading this article! If there are any other questions or comments we can help with, please don’t hesitate to reach out in our comment section below.
