The SQL TRUNCATE / SQL SERVER TRUNCATE command is a data definition language statement that can delete all the information from an existing database table without removing the table itself. This will free up space within the table, but users should remember that these changes may not be reversible on some databases. As it’s a DDL statement, there’s no need to commit each step – when you run this command, it automatically commits at completion. Use caution with this, as mistakes cannot generally be undone!
The TRUNCATE statement functions similarly to the DELETE statement, But you cannot use a WHERE clause when using this SQL TRUNCATE command.
Syntax
The basic syntax for the Sql Server Truncate statement is:
TRUNCATE TABLE table_name;
What Does the SQL SERVER TRUNCATE TABLE Statement Do?
The SQL SERVER TRUNCATE TABLE statement in SQL works by removing all rows from an existing table and resetting it to zero entries. This means that after running a truncate statement on the table, you will no longer have any row records stored there.
When you truncate a table, its structure of it, including columns, indexes, constraints, and relationships, is still intact. It’s similar to erasing data from a table but leaving the overall shape in place.
SQL Truncate Example
Let us take an example for a better understanding of SQL server truncate statements. Here are the Person table details:
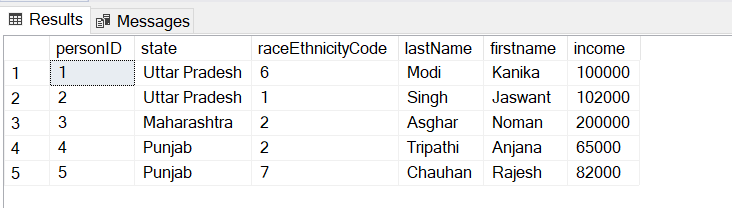
Now, let us run the SQL truncate statement.
TRUNCATE TABLE Person; SELECT * FROM Person;
After running the above script, all the rows will be deleted.
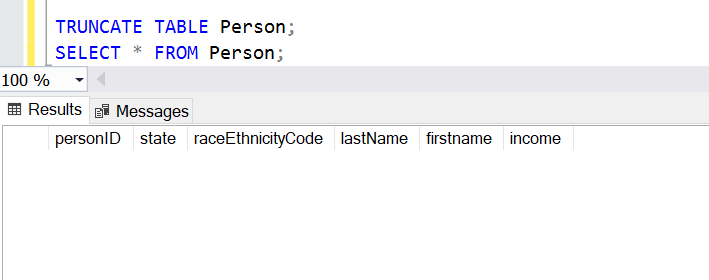
Note: The TRUNCATE clause doesn’t support the WHERE clause.
Truncating Large Tables
Microsoft SQL Server can delete or empty a table with more than 128 extents without acquiring locks. This makes it possible to truncate/drop large tables quickly and efficiently.
Conclusion:
This tutorial has provided the information needed to use SQL Server TRUNCATE TABLE statements to quickly remove all data from a table, especially if it is large. If you have any questions after reviewing this article, please comment in the comment section.
