SQL Database: In this blog post, we will discuss the SQL Database. As we know, our data are stored in a database, so if we want to know how to manage or manipulate the data of a database, then we must know about SQL databases.
What Is a SQL Database?
SQL stands for Structured Query Language. It’s used for relational databases. A SQL database is a collection of tables that stores a specific set of structured data.
SQL databases are relational Databases, which are collections of Highly Structured related tables with rows and columns using referential constraints like primary and foreign key relationships between tables.
SQL Database Table Structure
When a user stores data in a SQL server, then the data are stored inside the database in tabular format. Because in RDBMS, the tables are the fundamental database that stores the data in rows and columns.
Lets us take an example to understand the concept. Suppose we have created a student table. Then each row will be treated as a student’s record, and each table column will contain the corresponding student’s information like, ID Number, Name, Address, Class, and many more.
Rows: If you want to add data to a row in the database table, you can execute an SQL query. If the table has a primary key for any column, then in each row, that column will have a unique value, which helps avoid data duplication.
Columns: Each table contains specific attribute information and properties like Datatype and range. And also, some tables have the primary key, which helps identify an entity uniquely. If we take the Student table, then we can take the ID number column as our primary key because that’s unique for each record.
Benefits of using SQL database
Here are some of the key benefits of Using SQL Database
- High flexibility in modifying and organizing data
- Better data consistency across applications and instances
- Reduced data redundancy through normalization
- Improved performance through optimized memory usage and processor speed
- Ease of maintenance through built-in automation tools and customizable external monitoring options.
- Strong standard language and query capabilities for data retrieval and manipulation.
- High scalability and ability to handle large amounts of data
- Widely supported and used in various industries and applications.
SQL Database Types
Now let us discuss the various SQL database types:
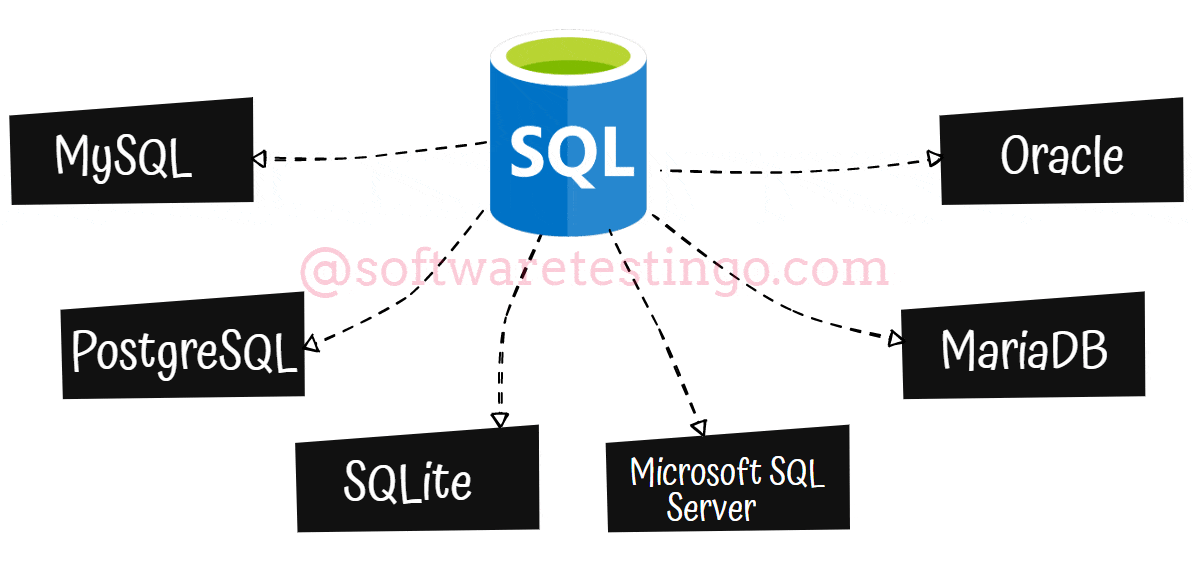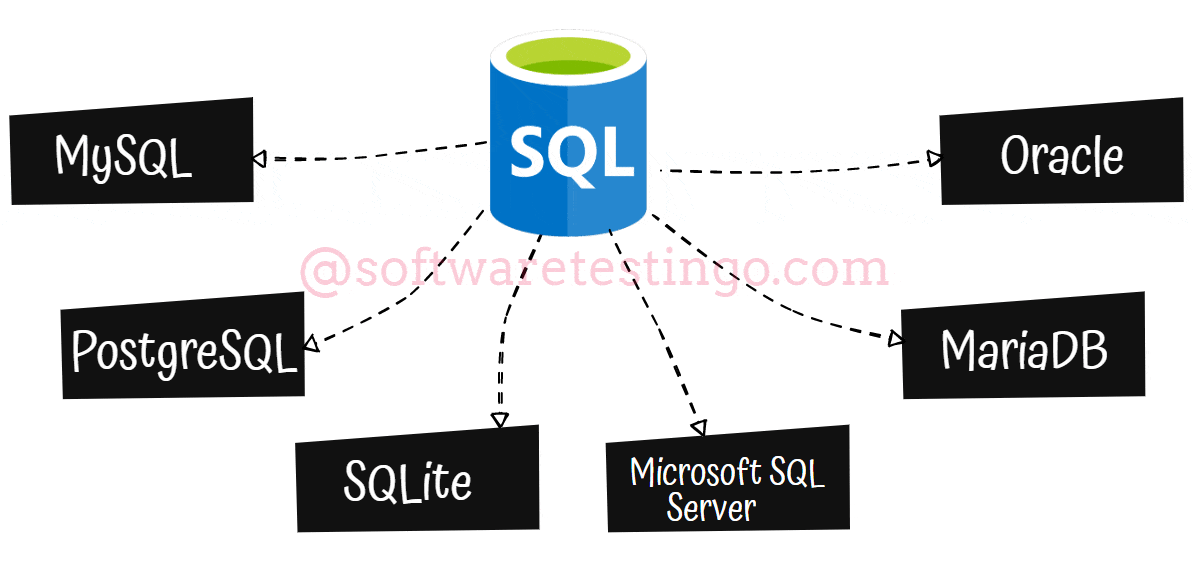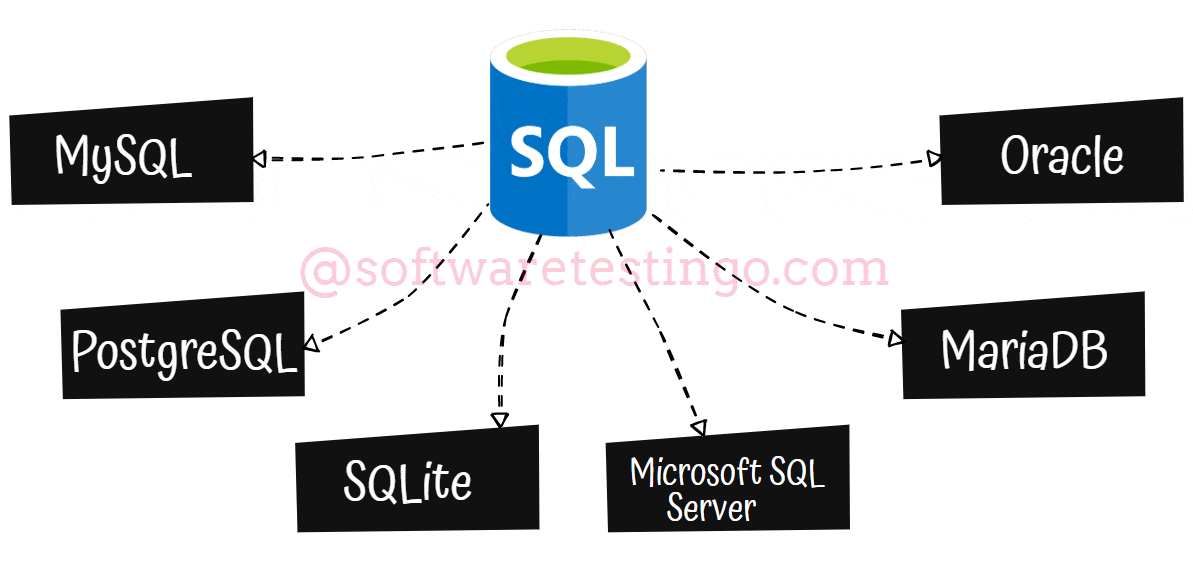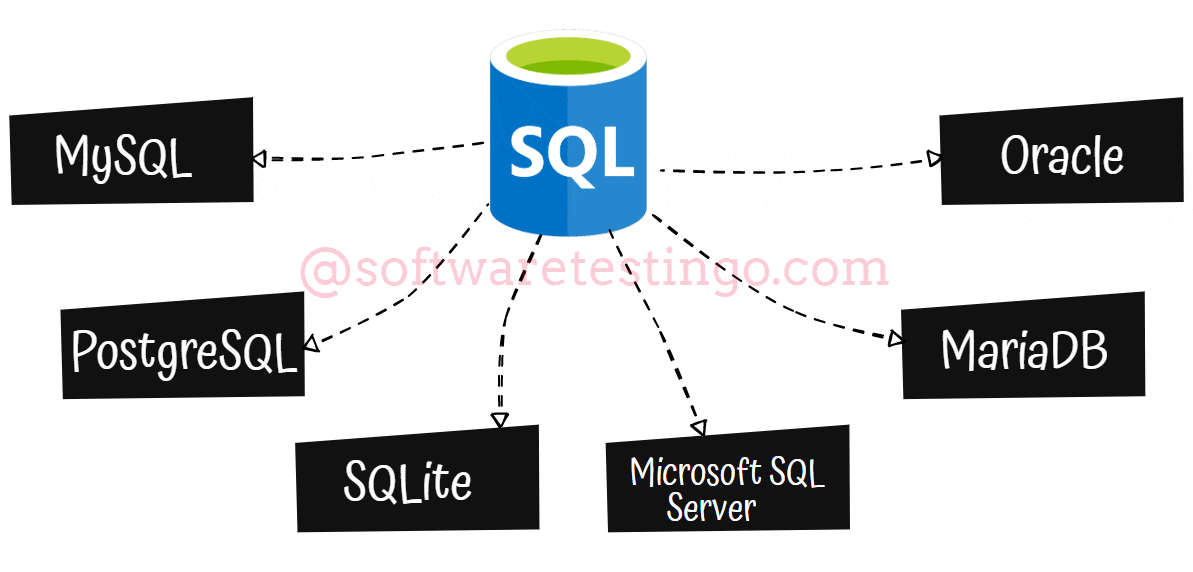
MySQL is a fully-managed database type that is very popular among SQL-based management. It was originally an open-source project built on C and C++, but Oracle Corporation has acquired it.
PostgreSQL is a type of database that is more advanced than MySQL database. PostgreSQL combines the traditional table-based approach with user-defined objects to create more resilient databases that support and analyze complex data. PostgreSQL is an open-source, freely accessible service owned by the PostgreSQL Global Development Group.
SQLite can be used within other applications to improve their storage capabilities. It is often used as the on-disk file format for financial analysis and cataloging applications.
The Microsoft SQL Server (MSSQL) is a popular DBMS with many innovative management solutions. T-SQL, which is derived from SQL, can be used to interact with MSSQL databases. The 2019 version of MSSQL comes with Apache Spark and Hadoop Distributed File System integration for extensive data management and analysis.
MariaDB: If you’re looking for an open-source fork of MySQL, MariaDB is a great option. It’s licensed under the General Public License, so it’s freely accessible to everyone. Plus, it’s a database management system in SQL that can be used as an alternative to MySQL DBMS.
Oracle: The Oracle relational database management system is a versatile tool supporting multiple workloads. This type of DBMS in SQL is commonly used for online transaction processing and data warehousing, making it a valuable asset for any business.
SQL Database Operations
With an SQL Database, we can perform various operations; out of them few are very important, and those are:
Let’s try to understand how to perform the above operations with an SQL Database one by one in detail.
SQL CREATE Database
While dealing with the database, the first thing to do is create a Database. In SQL, to create a database, both database developers and other users use this SQL statement to create a new database within the database management system. The specified name in the ‘Create Database’ statement will be used as the new database’s name.
SQL Create Database Command Syntax
CREATE DATABASE Database_Name;
In the above syntax, we can notice we have to mention the keyword first, CREATE DATABASE, and then we need to mention the database name. In this case, the database name we want to create is Database_Name.
Note:
- Database names should be simple, unique, and easily identifiable.
- Database name should not be more than 128 characters in length.
When we successfully execute the command, we get the below output.
Database created successfully
List All Databases In SQL Server
In DBMS, multiple databases will be present if someone wants to verify whether the database is created in the SQL server. To do so, you have to list all SQL databases, and you can use the below command.
SELECT * FROM sys.databases;
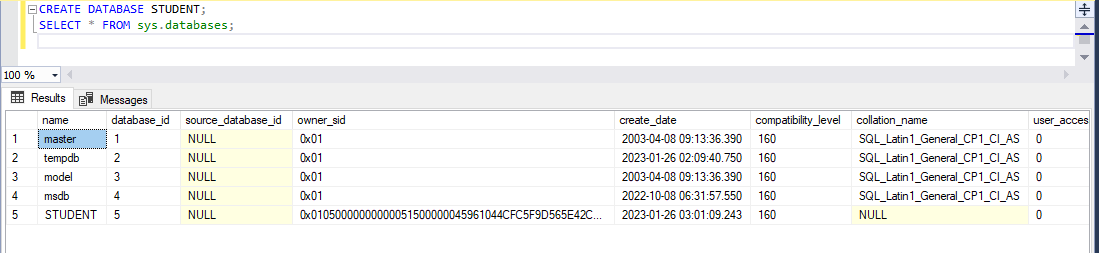
Note: This command will display both System Default databases and user-created databases.
SQL Create Database If Not Exists
SQL does not allow developers to create a database with the same name, and if you try to create a database with the existing database name in the same system. Then the “Create Database” statement will return an error.
For example, our database management system has a database called “STUDENT,” If you are trying to create a new database with the same name, “STUDENT”, you will get the below error in the console tab.
Database ‘STUDENT’ already exists. Choose a different database name.
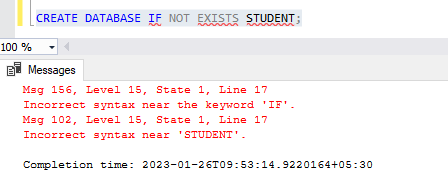
But we can avoid or handle this type of error with the help of CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS statement. When we use this CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS statement, it will create a new database if there is no existing database with the same name. For example,
CREATE DATABASE IF NOT EXISTS Database_Name;
But if you use the same statements, then we are getting below error
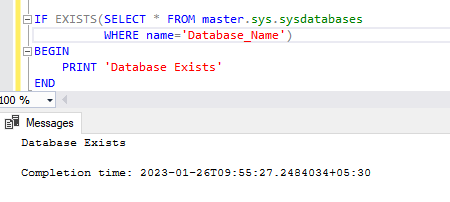
But still, we can verify the same by using the below statements. This will verify in the DBMS whether the mentioned Database name is present. If a Database is present on the mentioned name, it will print Database exits in the console.
IF EXISTS(SELECT * FROM master.sys.sysdatabases
WHERE name='Database_Name')
BEGIN
PRINT 'Database Exists'
END
SQL DROP Database
When we try to delete an existing database from the database management system, we need to execute the SQL Drop Database statement. While executing the below statement, remember that it will permanently delete all the tables and views from the database management system. So you have to be very careful while executing this SQL command.
Syntax DROP Database SQL
DROP DATABASE Database_Name;
In the above syntax, we have to specify the name of the database with the DROP DATABASE keyword to delete it from the Database management system.
We can also delete multiple databases with a single SQL statement. We must mention all those databases we want to delete from the DBMS and separate them by comma (,).
DROP DATABASE Database_Name1, [ Database_Name2, ......., Database_NameN ] ;
If you try to delete a database, but the database is not present in the DBMS, you will get the below error message in your console.
Can’t drop database ‘Database_Name’; database doesn’t exist
So we suggest always trying to execute the show command to List All Databases In SQL Server. If you do so, then you will never get the above error.
If an attempt is made to delete a currently used database, the “drop” statement will return an error message indicating that the database cannot be dropped because it is in use. Here is the error message.
Cannot drop database “name_of_the_database” because it currently in use
Note:
- Ensure you have admin or DROP permission before running the command to delete a database.
- This statement deletes all data from the database, so it is important to keep a backup before dropping the database.
- The database cannot be deleted if another user uses it.
SQL RENAME Database
The rename SQL server database statement is used in SQL to change the name of an existing database. This might be done for technical reasons because the original name is no longer relevant to the data contained within the database or sometimes if the developers want to give a temporary name to the database.
SQL Rename Database Syntax
When we want to change the name of the database, we can do that with the help of ALTER DATABASE statement or SP_RENAMEDB statement or by using SQL Server Management Studio. By using all these methods, we can rename the SQL server database.
SQL Rename Database By ALTER DATABASE
With the help of ALTER DATABASE statement, we can change the name of a database, and here is the syntax:
ALTER DATABASE olddbname MODIFY NAME= newdbname
SQL Server Rename Database By SP_RENAMEDB statement
To change the name of the database, we have another way. We can do the SQL Server Rename Database By SP_RENAMEDB statement, and here is the syntax for that:
EXEC sp_renamedb 'olddbname', 'newdbname'
SQL USE Database Command
In our Database management system, there will be many databases. When we are working with multiple databases that time we need to switch from one database to another database. to Switch from one database to another database, we need to execute the below statements:
USE my_db;
When we execute the above statement, the database will change from Database_Name to my_db, and all operations will be performed inside the my_db databases.
SQL Server Database Naming Conventions
Many tables will be inside databases, and many users are working on various tables. So if you follow a naming convention, that can help you find the required table and helps in efficient database management.
Here are some of the key points to remember for Naming Conventions:
- Names of database objects must begin with an alphabet or an underscore and contain alphanumeric characters.
- Avoid quotes and symbols such as @, #, and $ while naming objects.
- Use full English words and avoid abbreviations.
- Object names should not be a Transact SQL reserved word.
- Embedded spaces or special characters are not allowed.
- Avoid using prefixes like ‘sp_,’ ‘xp_,’ or ‘dt_’ to signify that they are system objects.
- Table and column names can be in ‘lower case,’ ‘UPPERCASE’, ‘Pascal Case’ or ‘camel Case’
- Avoid using spaces between words for table names and columns. Instead, use an underscore for joining multiple words.
- If a table represents a real-world entity, use nouns to name the table.
- Table names should be less than 126 characters.
- Table names can be either singular or plural.
- Avoid using prefixes like ‘tbl_’ for table names.
- Column names should be nouns that describe what is stored in the column.
- Column names should not use words that are just data types like text or date.
Conclusion:
Databases are one of the vital parts of the Database management system. Because without creating databases, we can not store our data. So if you are going to use databases in the future, you have to know the basic operations of databases, like How to use the SQL create database command, SQL drop databases command, and SQL Use Database Command in detail.
For More knowledge on SQL, you can follow the SQL tutorial blog post of softwaretestingo. We have written all the SQL concepts step by step; please let us know in the comment section if you have any questions about the above concepts.
