Maven Life Cycle: When we talk about a Maven Life Cycle, we mean a set of steps to do tasks. The Maven build life cycle is a set of steps to complete the tasks and goals of a Maven project. After each step, if everything goes well, we get the expected result.
In Maven version 2.0, the focus is on the build lifecycle. It says that Maven needs to follow different build life cycles to get the right result after completing a build.
| Post On: | Maven Life Cycle |
| Post Type: | Maven Tutorial |
| Published On: | www.softwaretestingo.com |
| Applicable For: | Freshers & Experience |
Maven Lifecycle Phases
Maven comes with three built-in maven phases:
You can run more than one lifecycle at a time with Maven, and each one works separately from the others. However, they must be done in a specific order. The entire lifecycle is described in the “component.xml” file in Maven’s core module.
Each phase has a specific goal. For example, phases like ‘build’ and ‘test’ do certain tasks to reach the phase’s goal.
Tasks/Goals During Maven Build Lifecycle
Here are some tasks done during the Maven build lifecycle:
- Resource Preparation: Copies of resources like configuration files are added to the build folder.
- Compilation: Compiles the source code.
- Packaging: Puts dependency JAR files into the build folder.
- Running Unit Tests: Tests the code.
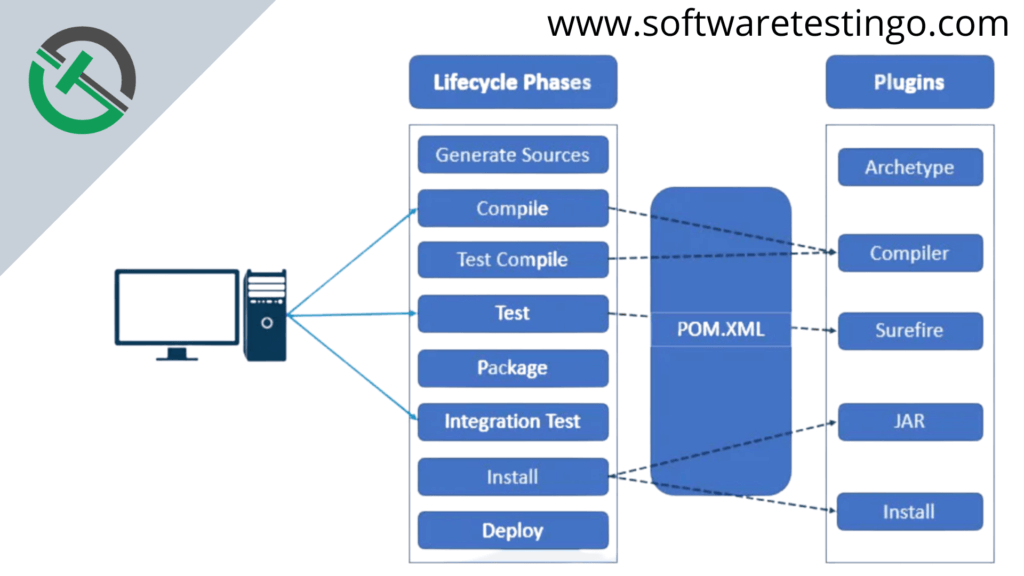
Let’s look at the different phases in more detail:
Clean Life Cycle
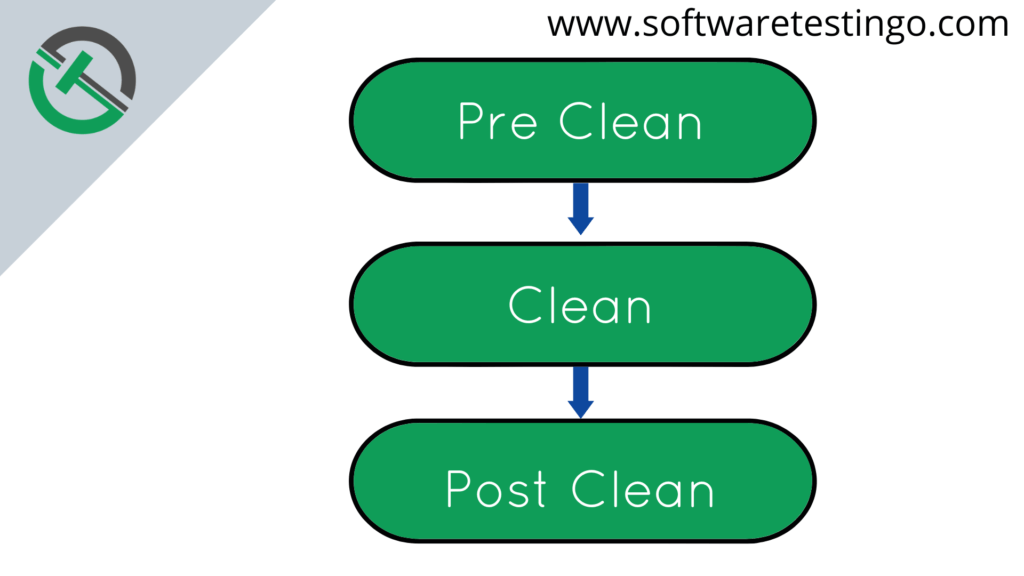
The Clean Life Cycle is used to delete or clean the project directory (usually called ‘target’) and its contents to get ready for new compiling and deployment. The command for this is “mvn clean“.
The mvn clean command does several tasks to delete temporary files made during the build. Commands like “mvn pre-clean” and “mvn post-clean” also run when you use mvn clean.
- mvn pre-clean: Runs tasks before cleaning.
- mvn clean: Cleans the build and also runs pre-clean tasks.
- mvn post-clean: Runs tasks after cleaning.
When you run the mvn clean command, it does the pre-clean, clean, and post-clean steps in order.
- When you execute that time, maven will execute the mvn pre-clean and mvn clean commands.
- mvn pre-clean: It will execute the pre-clean only.
- mvn clean: It will execute both pre-clean and mvn clean commands.
- mvn post-clean: This will execute pre-clean, clean, and post-clean altogether.
Default Maven Life Cycle
This is the most typical and primary lifecycle of a maven. It starts with the validate phase, which checks that the Project is correct and all necessary information has been provided, and ends with the deploy phase.
| Phase | Description |
|---|---|
| validate | It validates whether the Project is correct or not, and all necessary information is available to complete a build |
| initialize | It initializes the build state, for example, set properties or creating directories |
| generate-sources | It compiles the project’s source code. |
| process-sources | It processes the source code, for example, to filter any values |
| generate-resources | It generates the resources for inclusion in the package. |
| process-resources | It initializes the build state, for example, by setting properties or creating directories. |
| compile | It is done in an integration or release environment, and the final package is copied to the remote repository for sharing with other developers and projects. |
| process-classes | For example, it post-processes the generated files from compilation to do bytecode enhancement on Java classes. |
| generate-test-sources | It generates any test source code for inclusion in compilation. |
| process-test-sources | It processes the test source code, for example, to filter any values. |
| generate-test-resources | It creates the resources for testing. |
| process-test-resources | It copies and processes the resources into the test destination directory. |
| test-compile | It compiles the test source code into the test destination directory |
| process-test-classes | For example, it post-processes the generated files from test compilation to do bytecode enhancement on Java classes. |
| test | It runs tests using a suitable unit testing framework. These tests should not require the code to be packaged or deployed. |
| prepare-package | It performs any operations necessary to prepare a package before the actual packaging. This often results in an unpacked, processed version of the package. |
| package | It installs the package into the local repository for use as a dependency in other local projects. |
| pre-integration-test | It performs actions required before integration tests are executed. This may involve things such as setting up the required environment. |
| integration-test | It runs checks to verify the package is valid and meets quality criteria. |
| post-integration-test | It performs actions required after integration tests have been executed. This may include cleaning up the environment. |
| verify | It processes and deploys the package, if necessary, into an environment where integration tests can be run. |
| install | If necessary, it processes and deploys the package into an environment where integration tests can be run. |
| deploy | It initializes the build state, for example, by setting properties or creating directories |
Note: If you execute the “mvn install” command, it will run all phases up to the install phase.
Each phase can be linked with zero or more plugin goals, and executing a particular phase is the same as running that phase’s plugin goals. For example, executing the install phase is like running the “install: install” goal.
But if you run the “mvn install” and “mvn install: install” commands, they’re not equivalent because “mvn install” will also execute all of the phases up to the install phase.
So, maven would also execute every goal associated with each prior phase, whereas “mvn install: install” would only execute this maven goal.
Here is the list of some of the most commonly used phased and attached goals.
| Phase | plugin: goal |
|---|---|
| process-resources | resources: resources |
| compile | compiler: compile |
| process-test-resources | resources:testResources |
| test-compile | compiler:testCompile |
| test | surefire: test |
| package | ejb:ejb or ejb3:ejb3 or jar:jar or par:par or rar:rar or war:war |
| install | install: install |
| deploy | deploy: deploy |
Site Maven Lifecycle
With Maven, you can clean and compile the source code and create a deployable application. Besides that, Maven has a “Site” phase, which does more than the Clean and Default phases.
The Site phase is important because it generates detailed documentation of the project and prepares reports. Maven has a specific lifecycle for this, with four phases.
- pre-site: Executes processes before the project site generation
- site: Generates the Project’s site documentation
- post-site: Executes processes to finalize the site generation
- site-deploy: Deploys the generated site to the web server
There are also plugin goals attached to the site life cycle phase, which are:
- site ( site: site)
- site-deploy ( site: deploy )
This command “mvn site” will generate the Javadocs for the Project. When you call this command, it is called “Doxia” document generation and other reporting plugins.
Conclusion:
Understanding the Maven build lifecycle is important for managing and automating the build process in Java projects. Whether you are cleaning up your project, compiling code, or creating documentation, Maven’s structured approach ensures that each task is done correctly and in the right order.
By learning the Clean, Default, and Site phases, you can make your development process smoother and create better applications.
Share this knowledge with your friends and colleagues to help them improve their development skills and use Maven’s powerful tools. Please spread the word and help others discover the full potential of Maven in their projects!
FAQ On Interview
[sp_easyaccordion id=”67662″]
