The Map interface in Java is a way of representing a mapping between a key and a value. It is often misunderstood to be part of the Collection interface. This article will help you understand how maps work in Java.
| Post On: | Map In Java |
| Post Type: | Java Tutorials |
| Published On: | www.softwaretestingo.com |
| Applicable For: | Freshers & Experience |
| Get Updates: | SoftwareTestingo Telegram Group |
What is the Java Map Interface?
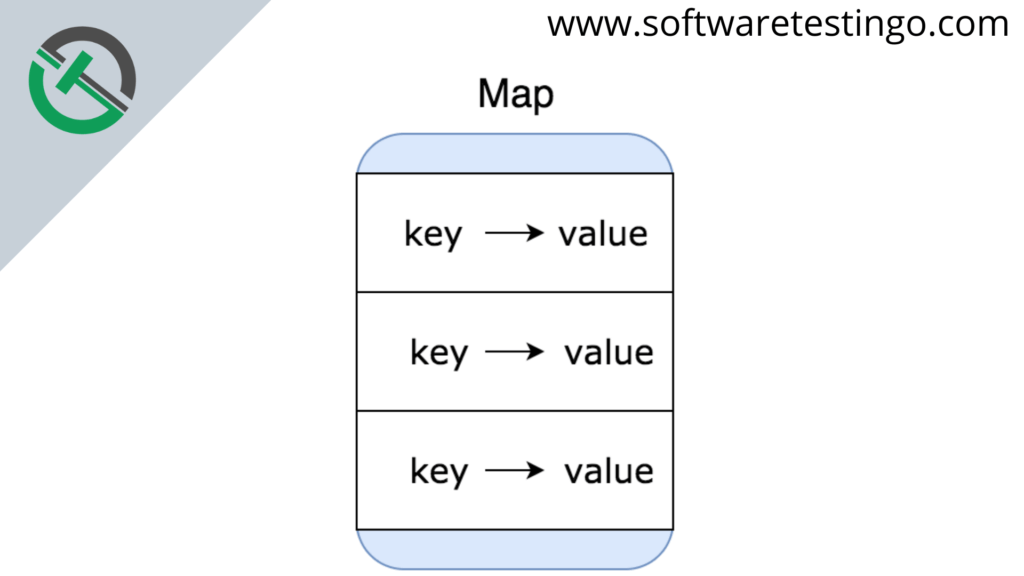
The Map interface in Java is a part of java.util package, and it stores data in key-value pairs. It does not allow duplicate keys. Some might misunderstand the Map interface as a subtype of the Collections interface, but that is not true. The Map interface functions differently from the Collection interface.
Why and when to use Maps?
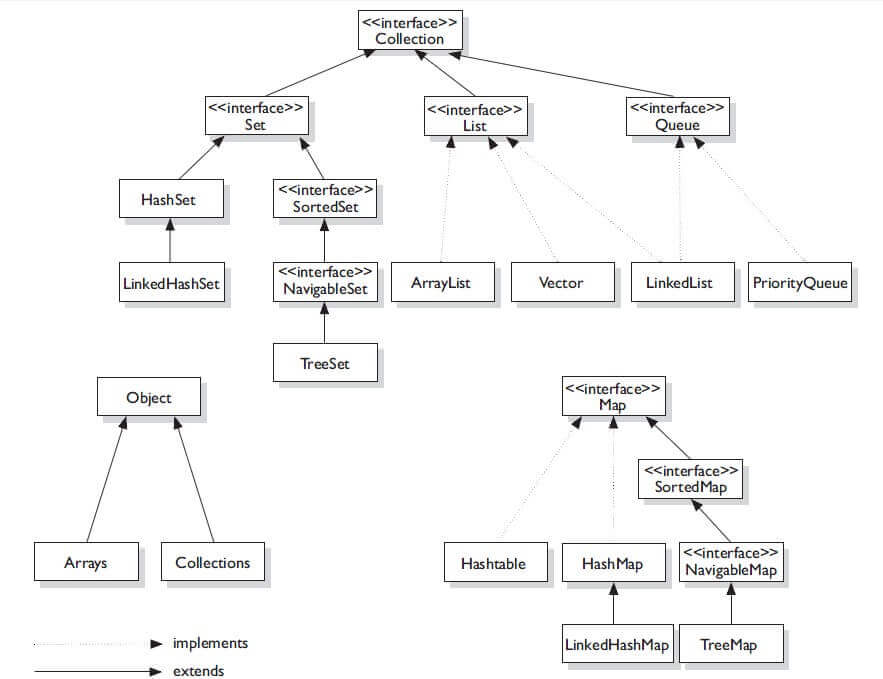
There are a number of classes in the Collections Framework that implement the Map interface. Each class has different functionality and level of thread safety. The most common implementation is HashMap, so we’ll be using this for most of our examples.
Working of Map
In Java, elements of Map are stored in key/value pairs. Each key corresponds to a unique value. A map cannot contain duplicate keys; each key can only be associated with one value.
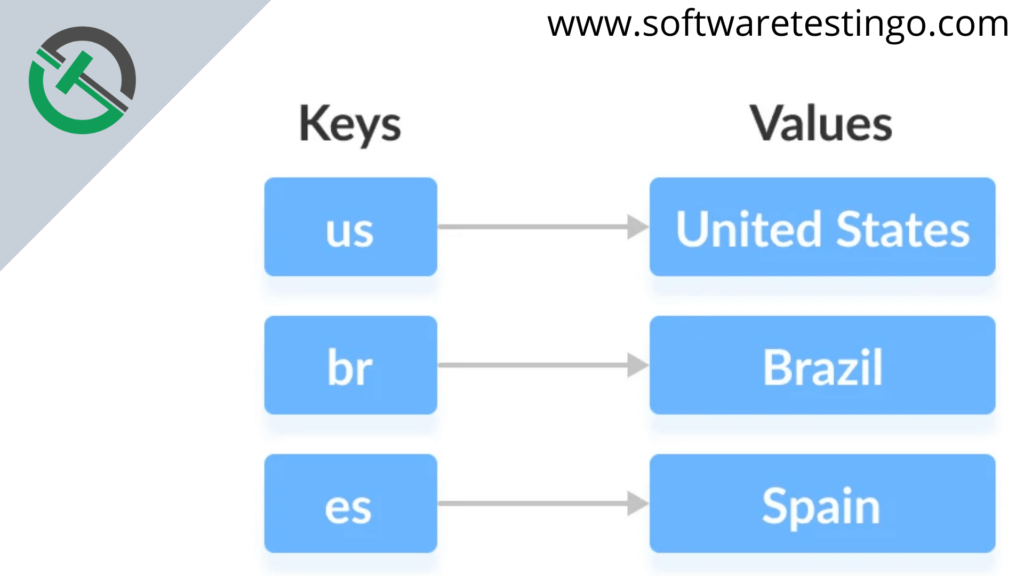
In the above diagram, we have two columns called Keys and Values. Now, if you want to access any value, you need a key’s help.
Classes that implement Map
The map is an interface, so we cannot create objects from it directly. To use the functionality of the map, we have to use those classes which have implemented the map interface. Such as:
- HashMap
- EnumMap
- LinkedHashMap
- WeakHashMap
- TreeMap
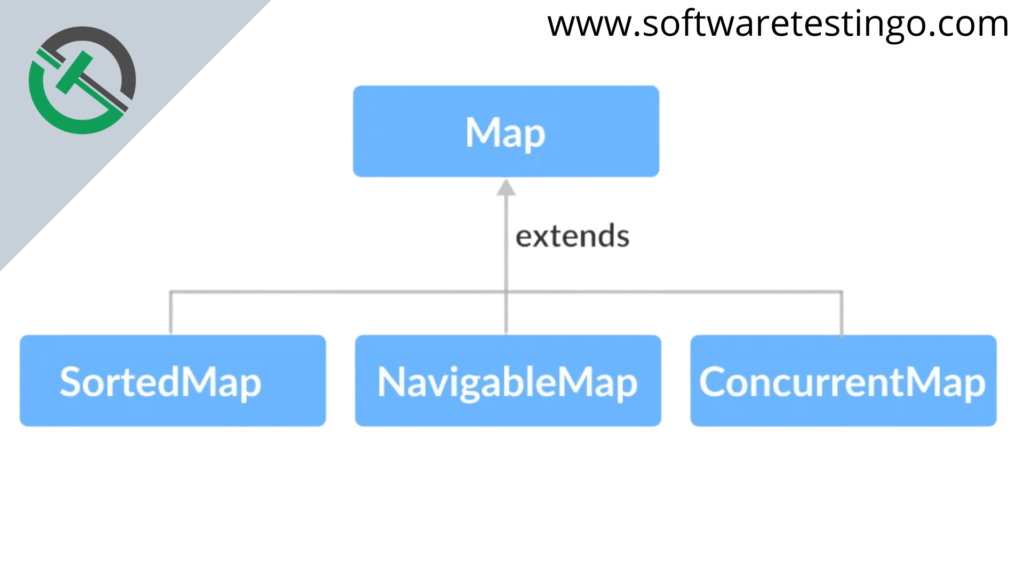
Interfaces that extend Map
The Map interface has several subinterfaces, including the following:
- SortedMap
- NavigableMap
- ConcurrentMap
Methods of Map
To use Map in Java, we must first import the java.util.Map package. Once imported, we can create a map by following these steps:
// Map implementation Map<Key, Value> numbers = new HashMap<>(); Map<Key, Value> numbers = new LinkedHashMap<>(); Map<Key, Value> numbers = new TreeMap<>();
The Map interface in Java can be used with the implemented classes to perform various operations. Some of these primary operations include:
- Adding elements
- Removing elements
- Changing elements
- Iterating through the map
Adding Into Map
The example below shows how to use the put() method to add elements to a map. The HashMap class is used here to implement Java maps.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapAdding
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Default Initialization of a Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Initialization of a Map using Generics
Map<Integer, String> hm2= new HashMap<Integer, String>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Software");
hm1.put(2, "Testingo");
hm1.put(3, "Blog");
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Java");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "Linux");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Data Structures");
System.out.println(hm1);
System.out.println(hm2);
}
}
Changing Elements:
If we want to change an element after adding it, we can use the put() method again. Since elements in a map are indexed using keys, we can change the value of a key by simply inserting the updated value for that key.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapChanging
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Default Initialization of a Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Software");
hm1.put(2, "Testingo");
hm1.put(3, "Blog");
// Before Change
System.out.println("Before Chganging Elements: "+hm1);
hm1.put(3, "Software");
// After Change
System.out.println("After Chganging Elements: "+hm1);
}
}
Removing Elements
You can use the remove() method to remove an element from a Map. This method takes in a key value and removes the mapping for that key from the Map if it is present.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapRemoving
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Default Initialization of a Map
Map<Integer, String> hm1 = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm1.put(1, "Software");
hm1.put(2, "Testingo");
hm1.put(3, "Blog");
// Before Change
System.out.println("Before Chganging Elements: "+hm1);
//Removing the Element
hm1.remove(3);
// After Change
System.out.println("After Chganging Elements: "+hm1);
}
}
Iterating through the Map
There are several ways to iterate through a Map. The most common way is to use a for-each loop and get the keys. The value of each key can be found using the getValue() method.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.HashMap;
import java.util.Map;
public class MapIterating
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Default Initialization of a Map
Map<Integer, String> hm2 = new HashMap<>();
// Inserting the Elements
hm2.put(new Integer(1), "Java");
hm2.put(new Integer(2), "Linux");
hm2.put(new Integer(3), "Data Structures");
for(Map.Entry element: hm2.entrySet())
{
int key=(int) element.getKey();
String value=(String) element.getValue();
System.out.println(key +"--> "+value);
}
}
}
