In this blog post, we are going to discuss What is Cloning in Git or Git Clone, but before learning, if you have referred to the previous tutorials where we have discussed Git Fork or Forking in GitHub, then those will make you comfortable in understanding the git Clone concept easily.
If you have no prior working experience with Git, then such people think Git Fork and Git Clone both are similar. Actually, there are a few similarities between these two, but also some differences are also there. So it’s suggested that first, you learn about Git Fork, and then you try to learn Git Clone so that you can easily understand the differences and similarities.
Since the basics of Git and GitHub have already been covered in our previous blog posts, now, in this blog post, we are going to understand the following:
- What is Git Clone or Cloning in Git?
- Why Clone a Repository?
- How does Cloning in Git work?
What is Git Clone or Cloning in Git?
If you want to create a copy of a remote repository on your local machine, you can use the git clone command. By default, this command will save your code in a local machine folder with the same name as your repository, but the remote git repository remains unchanged.
If you have made some changes and committed to your local repository (cloned repository), then those changes will not reflect on your remote repository. But you can synch your changes with a remote repository anytime.
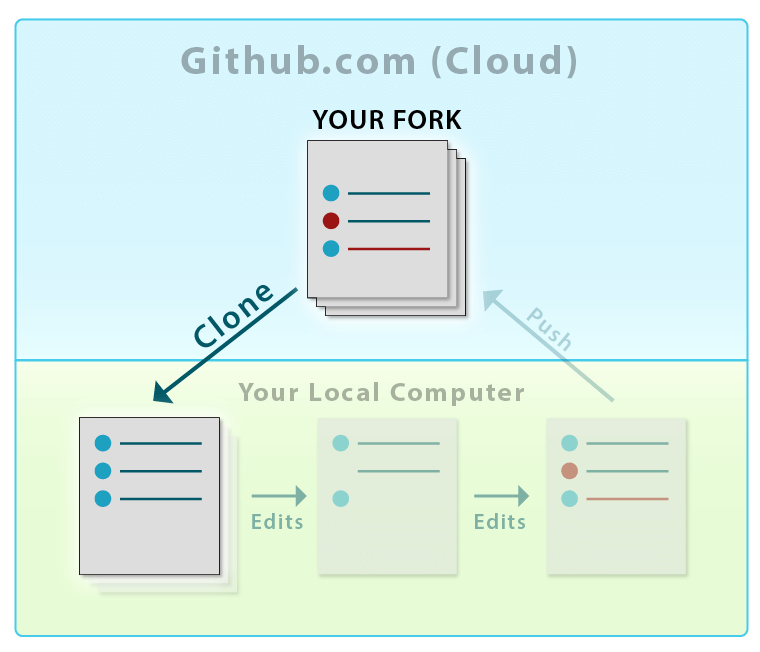
However, if you want to choose a different name for the folder that holds your cloned code, you can specify it after the URL of the repository.
Why Clone a Repository?
As we mentioned, whenever we clone a repository, it will download all the complete source code into your local system, but let us try to understand by taking some real-time examples for a better understanding of why Git Clone is required.
Contribute to Organizational Projects: You’ll need a centralized system if you work on a code base with multiple people. Cloning can help with this by allowing people to edit the project code to fix issues or add features. This results in better software being produced in less time with greater collaboration.
Make use of Open Source Repositories: If someone wants to use functionality that has already been developed, they should look into open source repositories as these often have what people are looking for. This way, people can save time and resources.
Cloning is a vital part of the Git and GitHub experience, so let’s take a closer look at how it works. It’s actually quite simple and straightforward, as we’ll see now.
How does Cloning in Git work?
If you’re looking to set up a shared repository for your development team, GitHub/ GitLab/ BitBucket are all great platforms offering online collaboration repositories. These types of repositories are called Upstream Repositories or Central Repositories.
The central repository is the most up-to-date version of itself, containing all changes from all contributors. Sometimes, it’s referred to as the original repository.
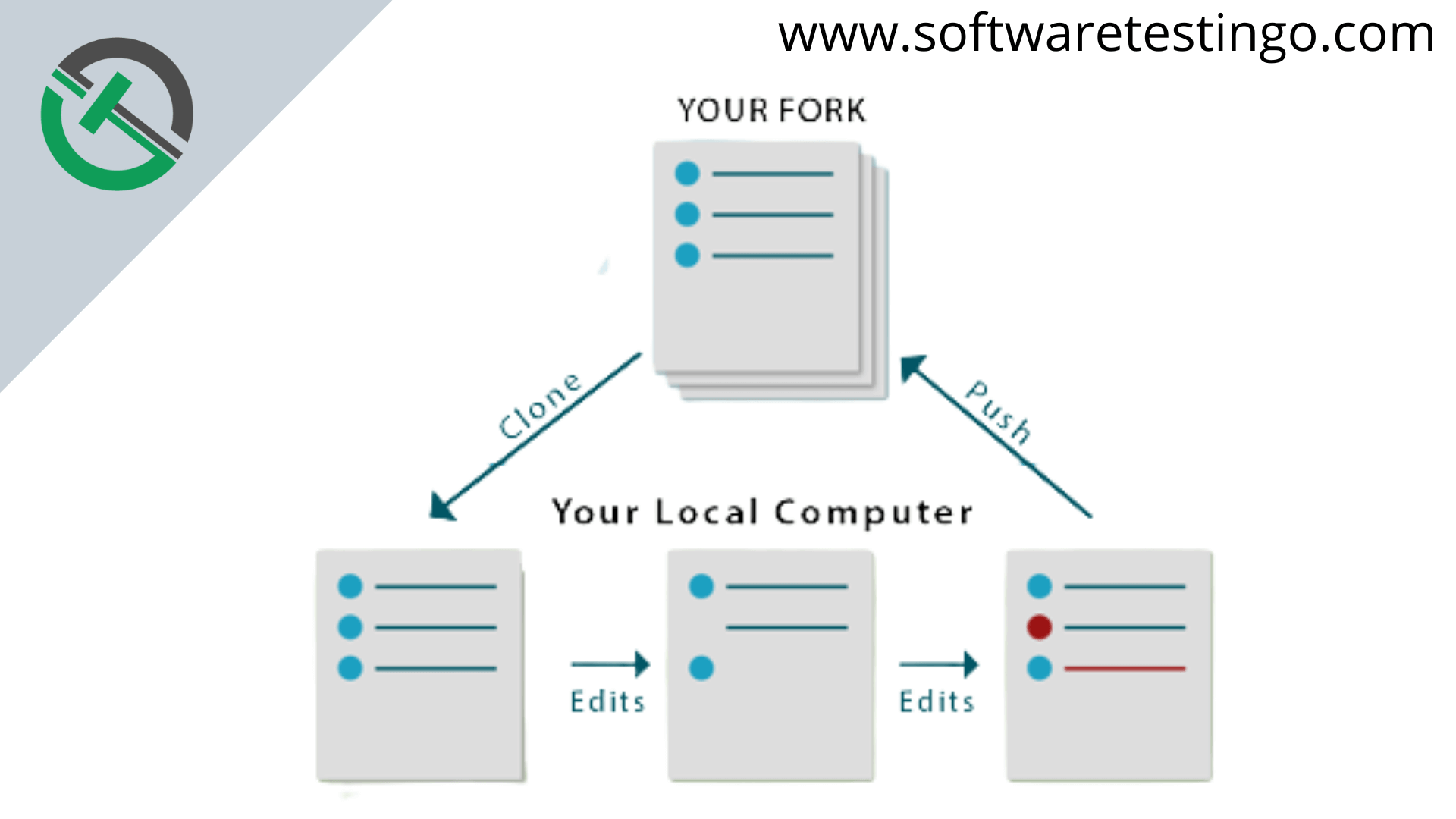
As you see, the Git Clone process has gone through the below phases:
Clone a Repository: If you’re interested in contributing to a project, you can start by cloning the upstream repository onto your local machine. Cloning creates an exact copy of all the project files on your system so that you can make changes without affecting the original codebase.
Make the desired changes: After cloning, you can provide your contribution to the repository. Your contribution can be in the form of editing the source files, resulting in either a bug fix, adding functionality, or maybe optimizing the code. But remember, everything happens on your local system first.
Pushing the Changes: By making changes and then pushing them to the upstream repository or central repository, you can keep everyone up-to-date with the latest modifications.
Git Clone
You can clone a Git repository either from your own account or someone else’s. In the following section, we will clone the demo repository that is available on my GitHub account. You can create a new GitHub repository and try cloning it yourself to get some practice.
How to Clone a Repository or use Git Clone Command?
Before cloning a repository from GitHub, please ensure you have a repository on your GitHub account. To clone a repository, follow the steps below:
If you want to clone a repository, go to the page for that repository. You can find repositories on your dashboard in the sidebar.
Click on the demo repository link, and It will redirect you to the repository page.
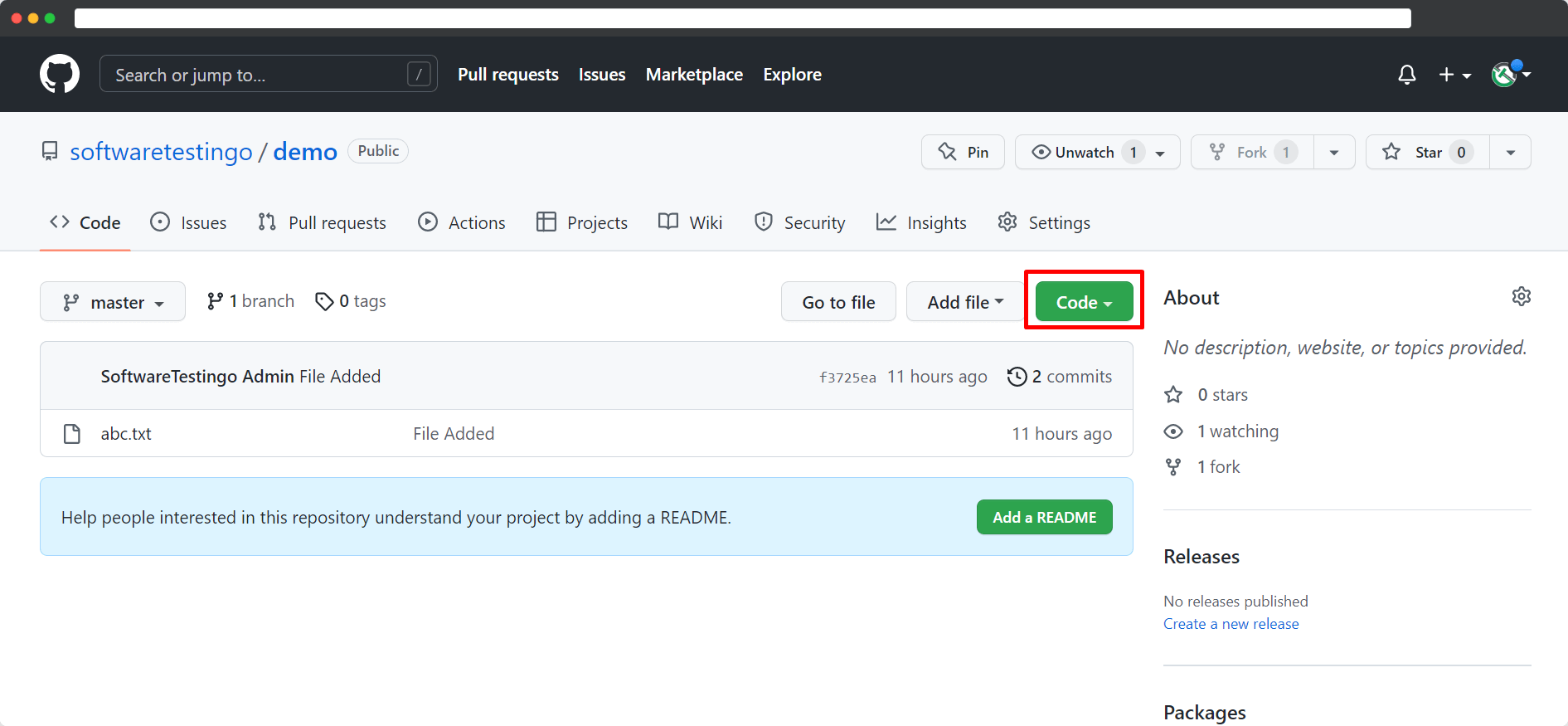
Press the code button. After pressing the code button, it will open a popup.
From that popup, we need to copy the URL; you can do this by clicking the icon that is present beside the URL.
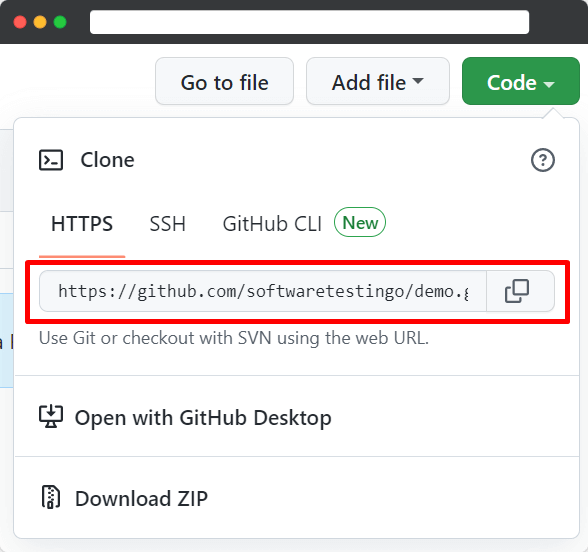
After copying, the URL opens your Git Bash on your system.

Note: Be sure to change the directory to where you want the repository cloned. I have my directory, Git Repo democlone, marked in the image. That is where I will be cloning the repository from GitHub.
Go to the directory where you want to clone the repository, but before that, you can check if any files or directories are already present. You can do that by running the ls command like below.

If there are any repositories or files, then those will be listed when you execute the ls command. Enter the following git clone command to clone the repository.
git clone
Example: git clone https://github.com/softwaretestingo/demo.git
Here, the URL is the same URL that we copied in our above steps (from the GitHub URL).
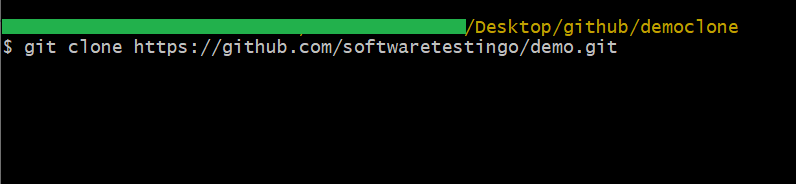
Note: If you’re having trouble accessing your repository on GitHub Cloud, try typing ‘Git URL’ into the address bar in your browser. This should take you to the repository page.
The following message will appear when you press the enter key. Cloning the repository into your system will take a few seconds or minutes based on the file size.
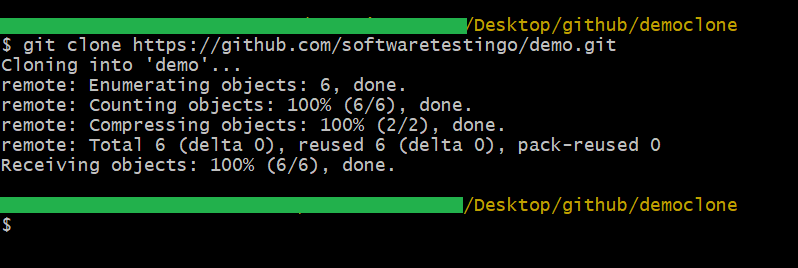
Note: If you’re having trouble accessing a GitHub repository, try checking the repository’s RL. You can do this by typing the RL into your browser’s address bar. If the repository page opens, then you should be able to access it.
After the completion of the Cloning process, the user can validate or confirm by executing the ls command.

For our example, we have taken the central repository as a demo. So the same is downloaded to our local system.
We can also confirm this by manually navigating our local system.
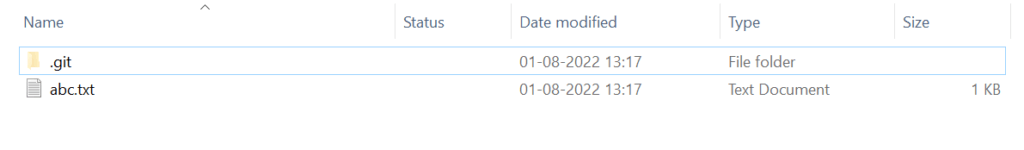
As you can see, we were able to clone the repository from GitHub. This is helpful because now we can work on the files locally, like with any other code file. Cloning is a very useful tool that is used frequently by those who develop software using Git or GitHub.
Once changes are made, the user pushes them back up to the original repository on GitHub, making it available to everyone else watching or contributing to it.
