Exception Handling In Java: Exception handling is an important aspect of software development in Java. Exceptions are errors or unexpected events that can occur during the execution of a program, and handling them properly is critical for ensuring the stability and reliability of the software.
Java provides a robust system for handling exceptions through its built-in exception-handling mechanism. With exception handling, developers can catch and handle errors at runtime, providing users with a more graceful and informative response to issues that may arise.
Exception Handling In Java
Exception handling in Java allows for custom exception classes, enabling developers to define and handle errors specific to their application’s domain. Proper exception handling can improve a Java application’s robustness, reliability, and maintainability.
In this post, we will learn about exceptions, such as Exceptions, Exception Hierarchy, the difference between errors and exceptions, and different types of exceptions with Java program examples.
Errors In Java Program
In Java mainly, there are 3 types of errors in java program:
- Compile-time errors
- Run time errors
- Logical errors
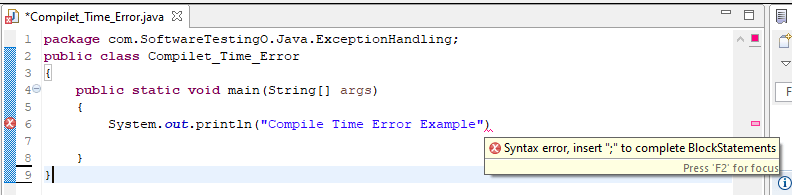
Compile-time errors: When we write the program, there is a possibility of some syntactical errors due to the program’s failure to compile. some examples of syntactical errors are missing the semicolon at the end of the Java statements; writing statements without proper syntax will generate a compile-time error.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling;
public class Compilet_Time_Error
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Compile Time Error Example")
}
}
When you try to compile the Java program, you will get the compile-time error, which states.
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.Error: Unresolved compilation problem: Syntax error, insert ";" to complete BlockStatements at com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling.Compilet_Time_Error.main(Compilet_Time_Error.java:6)
Run time errors: This type of error is generated when a computer system is not efficient in executing a particular statement, like insufficient memory to store something or the inability of the microprocessor to execute some statements.
Example1: Runtime Error caused by dividing by zero
package com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling;
public class Run_Time_Error
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int var1=10;
int var2=0;
//This statement cause the runtime error
int var3=var1/var2;
System.out.println("The Valued of Var3:- "+var3);
}
}
Error Message in Console:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArithmeticException: / by zero at com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling.Run_Time_Error.main(Run_Time_Error.java:11)
Example 2: Runtime Error caused when we are trying to Assigning/Retrieving Value from an array using an index that is greater than the size of the array
package com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling;
public class Run_Time_Error
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int arr[]=new int[5];
//Below statement cause the Runtime Error
//Bcoz we are assign the value to 7 index where as our Array Max index is 5
arr[7]=123;
System.out.println("Sucessfullt Assigned the Value");
}
}
Error Message In Console:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException: 7 at com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling.Run_Time_Error.main(Run_Time_Error.java:12)
Logical Error: These types of errors are generated because of flaws in the logic of the program; the program might be using a wrong formula, or the design pattern of the program itself is wrong. The Java compiler or the JVM does not identify this type of error, and the programmer is only responsible for such errors.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.Java.ExceptionHandling;
public class Logical_Error
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int a=10;
//Because of Below Statement (wrong logic) we are not getting the expected result
if(a>=10)
{
System.out.println("The Value of A Is Less then 10");
}
else
System.out.println("The Value of A Is Greater then 10");
}
}
Output:
The Value of A Is Less then 10
What is an Exception?
When we are executing our program at that time, due to some unwanted or unexpected event, the normal flow of the program is interrupted. We get a system-generated message when an exception is generated when the program flow is terminated from that statement. In Java, we can handle the exceptions and provide a meaningful message so the user can easily understand the reason for an exception.
Why an Exception Occur?
There are several reasons for occurring exceptions, but below are a few reasons that can generate an exception:
- A user has entered an invalid data
- File not found
- A network connection has been lost in the middle of communications
- The JVM has run out of memory
If an exception occurs, we need to handle that; otherwise, that may lead to a system failure. that’s why exception handling is one of the most important concepts of Java programming language.
Difference between error and exception
- Error: It can not be handled by the program. When it happens, the programmer cannot do anything.
- Exception: An Exception is an error that can be handled. It means when an exception happens, the programmer can do something to avoid harm to the application.
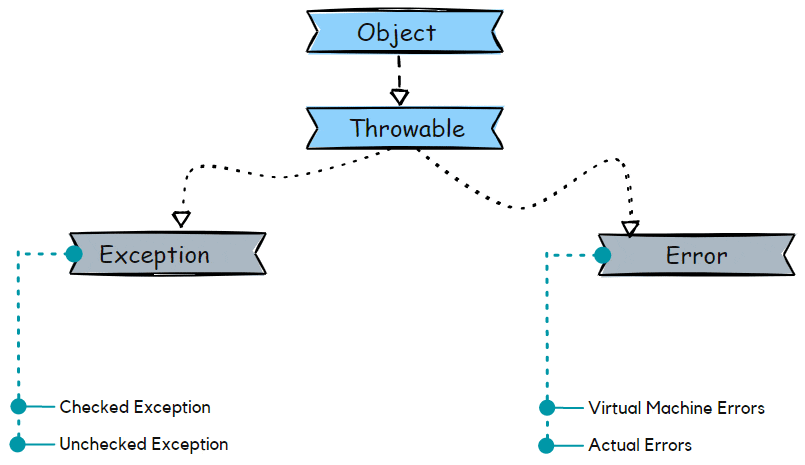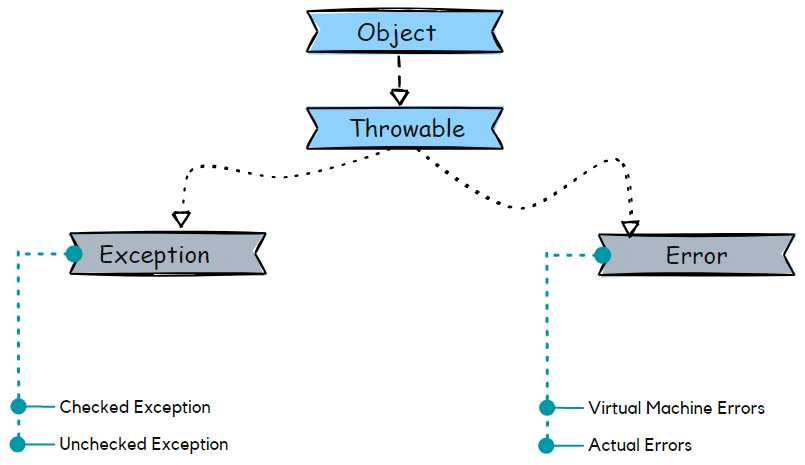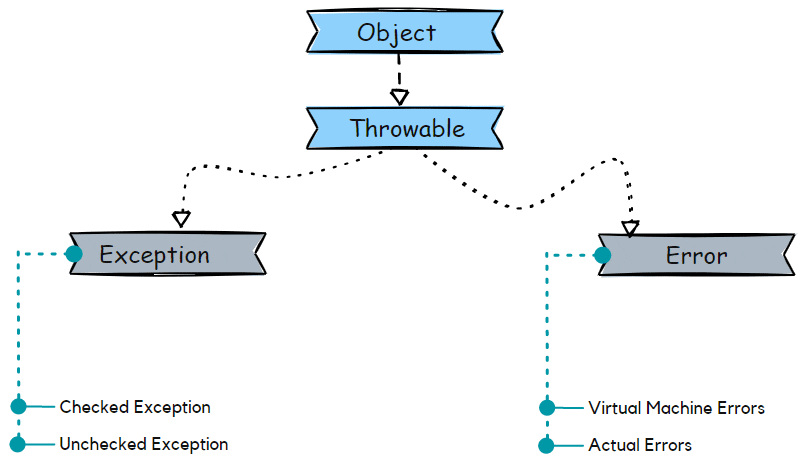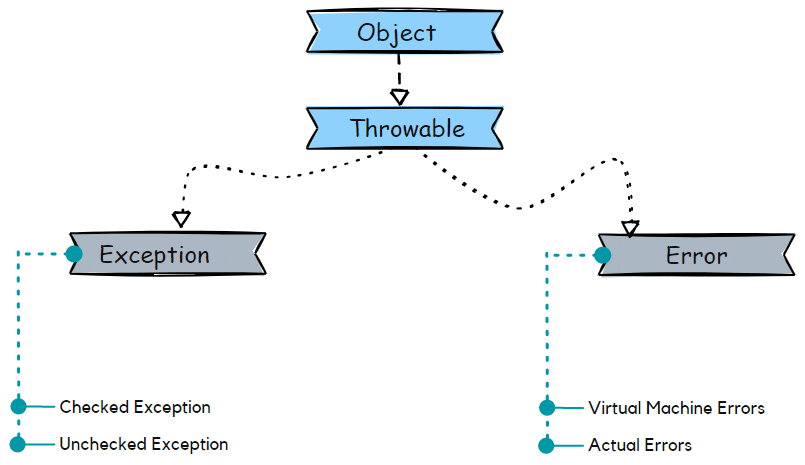
Exception Hierarchy
The base or root class of the exception hierarchy is Throwable; the base class is inherited by two subclasses, Error and Exception. See the below image for a better understanding of the hierarchy of exceptions.
Types of exceptions
There are mainly two types of exceptions in Java that are:
- Checked Exception
- Unchecked Exception
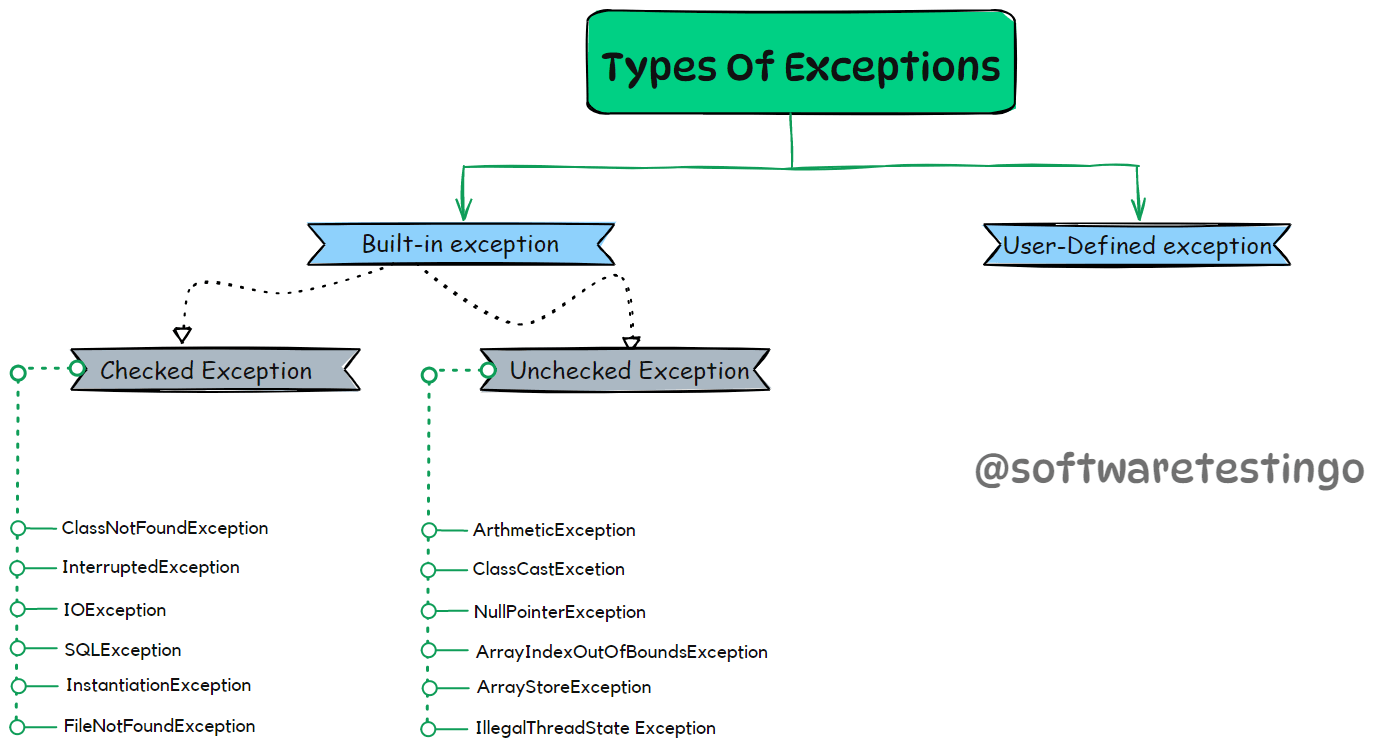
Checked Exception
The exceptions that are checked at compilation time by the Java compiler are called ‘checked exceptions’. If these exceptions are not handled in the program, you will get a compilation error—for example, SQLException, IOException, ClassNotFoundException, etc.
Unchecked Exceptions
The exceptions checked by the JVM are called ‘unchecked exceptions’ or Runtime Exception. these exceptions are not checked at compile time, so the JVM compiler doesn’t know whether exceptions are handled. So it’s the programmer’s responsibility to handle those exceptions or provide a safe exit. Some examples of unchecked exceptions are ArithmeticException, NullPointerException, ArrayIndexOutOfBoundsException, etc.
