In this tutorial, we will learn about the Deque interface and how to use it. We will also explore its methods.
Consider a queue in a bank. Ideally, people join the queue from the front or end and leave from either side. Sometimes, someone who just left the queue returns and joins the queue from the front. This is one of the real-time examples of queues where people can join and leave at both ends.
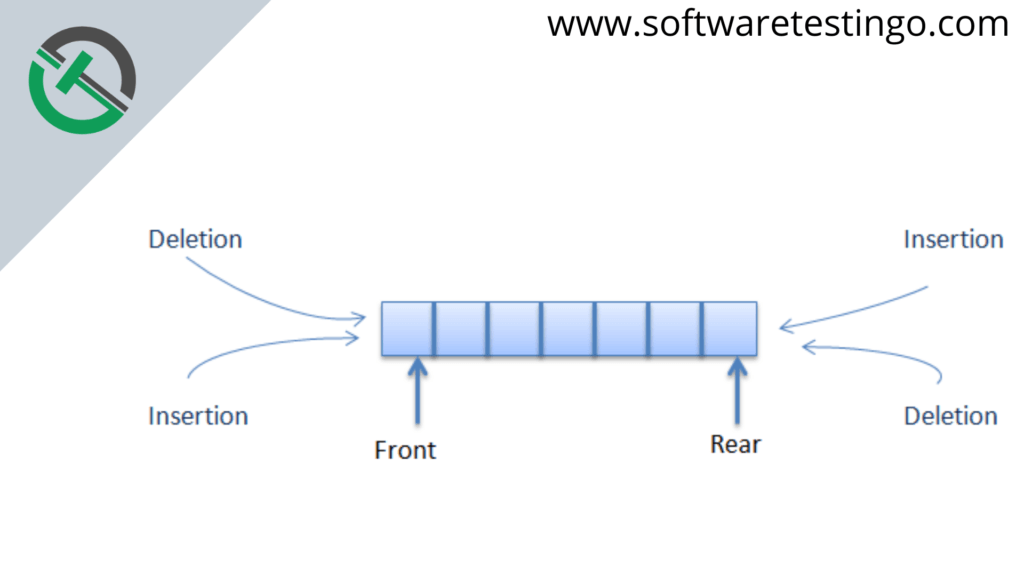
The Deque interface is a subtype of the queue interface. The Deque is related to the double-ended queue that supports adding or removing elements from either end of the data structure. It can be used as a queue (first-in-first-out/FIFO) or a stack (last-in-first-out/LIFO).
| Post On: | Deque In Java |
| Post Type: | Java Tutorials |
| Published On: | www.softwaretestingo.com |
| Applicable For: | Freshers & Experience |
| Get Updates: | SoftwareTestingo Telegram Group |
Classes that implement Deque
Java’s Deque interface is an interface, not a class. It only provides method declarations, so you can’t actually instantiate it. To create an instance of the Deque interface, you must provide concrete implementations for its methods. The classes that implement the Deque interface are:
- ArrayDeque
- LinkedList
- ConcurrentLinkedDeque
- LinkedBlockingDeque
How to use Deque?
A Deque in Java can be created by creating objects of the classes that implement the Deque interface. ArrayDeque and LinkedList are two common implementations of this interface.
// Array implementation of Deque Deque<String> animal1 = new ArrayDeque<>(); // LinkedList implementation of Deque Deque<String> animal2 = new LinkedList<>();
Methods of Deque Interface
With Deque in Java, you can easily add, remove, and retrieve elements. For example, we will try to understand how we can achieve that:
Adding Elements
We can use the add() method to add an element to a deque. The difference between a queue and a deque is that in a deque, the addition is possible from any direction; this allows us to access the two methods named addFirst() and addLast(), which are used to insert elements at either end of the Dequeue.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class DequeAdd
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing an deque
Deque<String> dque=new ArrayDeque<String>();
// add() method to insert
dque.add("To");
dque.addFirst("Welcome");
dque.add("Software");
dque.addLast("Testingo");
System.out.println(dque);
}
}
Removing Elements:
There are various methods available to remove an element from a deque. The deque interface provides us with the removeFirst(), and removeLast() methods. Apart from that, this interface also provides us with the poll(), pop(), pollFirst(), and pollLast() methods, where pop() is used to remove and return the head of the deque. However, poll() is used because it offers the same functionality as pop().
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
public class DequeAdd
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing an deque
Deque<String> dque=new ArrayDeque<String>();
// add() method to insert
dque.add("To");
dque.addFirst("Welcome");
dque.add("Software");
dque.addLast("Testingo");
//Display All the Elements Of Deque
System.out.println("Before Remove: "+dque);
System.out.println("Removed: "+dque.pop());
// remove the head and return it
System.out.println("Head Element: "+dque.poll());
System.out.println("After Remove: "+dque);
// First and Last Element
System.out.println("First element: "+dque.pollFirst());
System.out.println("Last Element: "+dque.pollLast());
//Display All the Elements Of Deque
System.out.println("Final Dequeue"+dque);
}
}
Iterating through the Deque
Since a deque can be iterated in both directions, the iterator method of the deque interface provides us with two ways to iterate—one from the front and one from the back.
package com.SoftwareTestingO.collections;
import java.util.ArrayDeque;
import java.util.Deque;
import java.util.Iterator;
public class DequeIterating
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Initializing an deque
Deque<String> dque=new ArrayDeque<String>();
// add() method to insert
dque.add("To");
dque.addFirst("Welcome");
dque.add("Software");
dque.addLast("Testingo");
for (Iterator itr = dque.iterator();itr.hasNext();)
{
System.out.print(itr.next() + " ");
}
System.out.println();
for (Iterator itr = dque.descendingIterator();itr.hasNext();)
{
System.out.print(itr.next() + " ");
}
}
}
Conclusion:
I hope you found this article helpful. In the remaining sections, we’ll explore more of Java’s features. Keep reading for more valuable content!
