Data Types In Java & Naming Conventions In Java: One of the fundamental concepts in Java and other programming languages is data types. Data types in Java determine the type of data a variable can hold, which can be either numeric, characters, or Boolean. Each data type in Java has a predefined size and a range of values it can store.
Understanding the various data types in Java is essential for any programmer as it determines how data is stored in memory, how it’s processed, and the range of operations that can be performed on it. In this article, we’ll explore the various data types in Java, their characteristics, and how they can be used to create robust and efficient Java programs.
Before we discuss the data types in Java, we will first try to understand the naming conventions in Java because a codder should know how to declare any variable, method, class, or package.
Naming Conventions In Java
Naming conventions in Java refer to rules or guidelines that developers use to name various program elements, such as variables, classes, methods, and packages. Following a consistent naming convention is essential as it makes it easier to read and understand code, improves code maintainability, and makes it easier for other developers to work with the code. In Java, there are several naming conventions that programmers should follow.

Types Of Naming Conventions
Here, we have listed some of the types of naming conventions that you should follow while writing your Java codes.
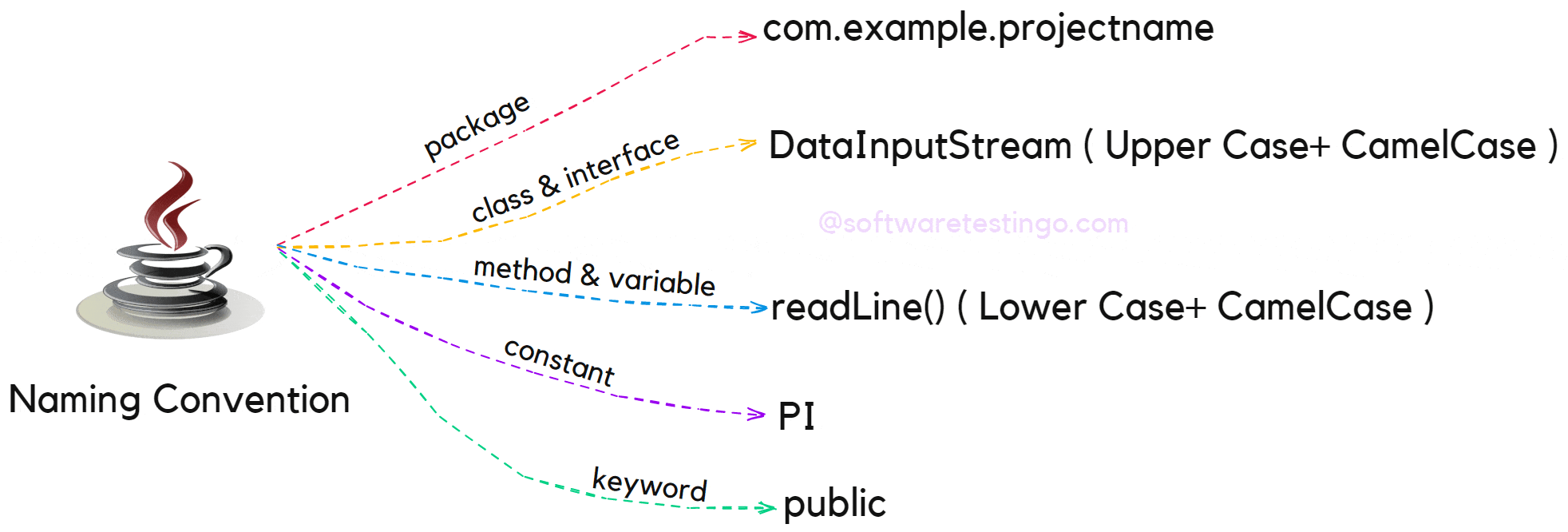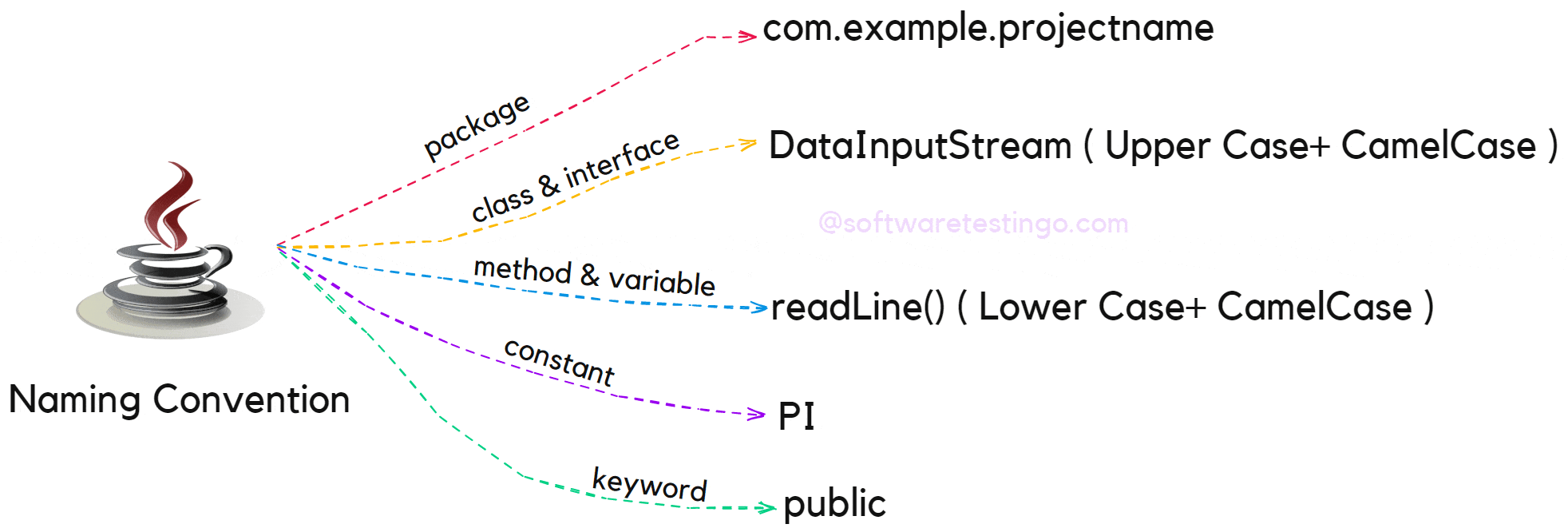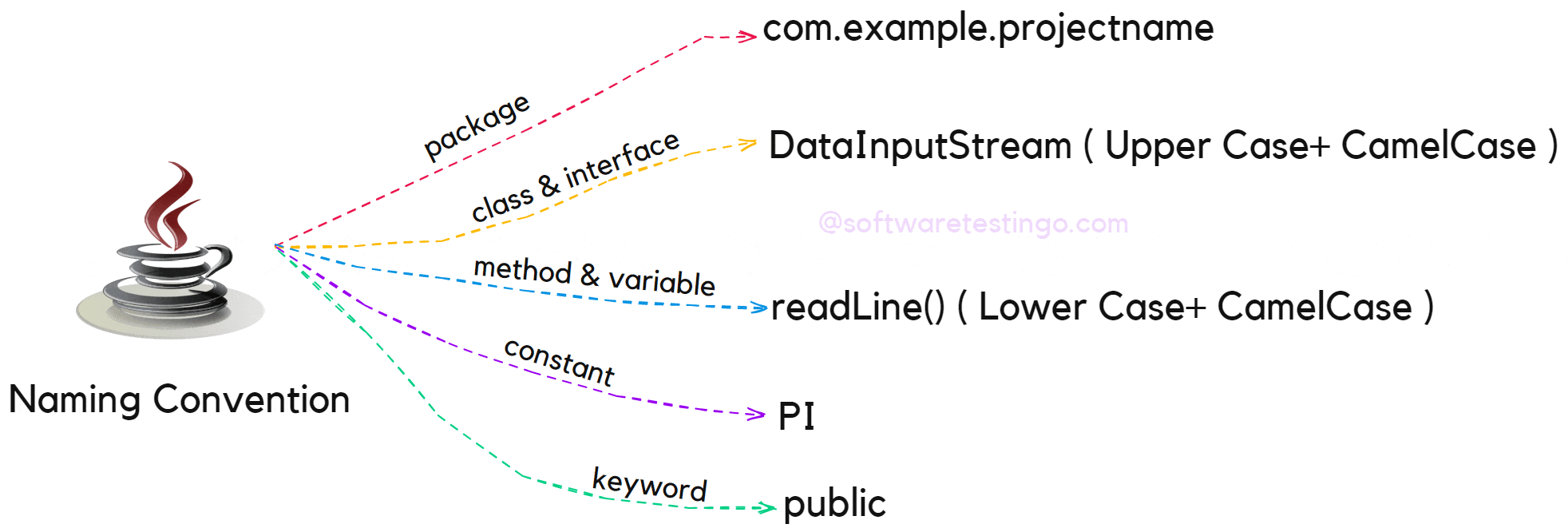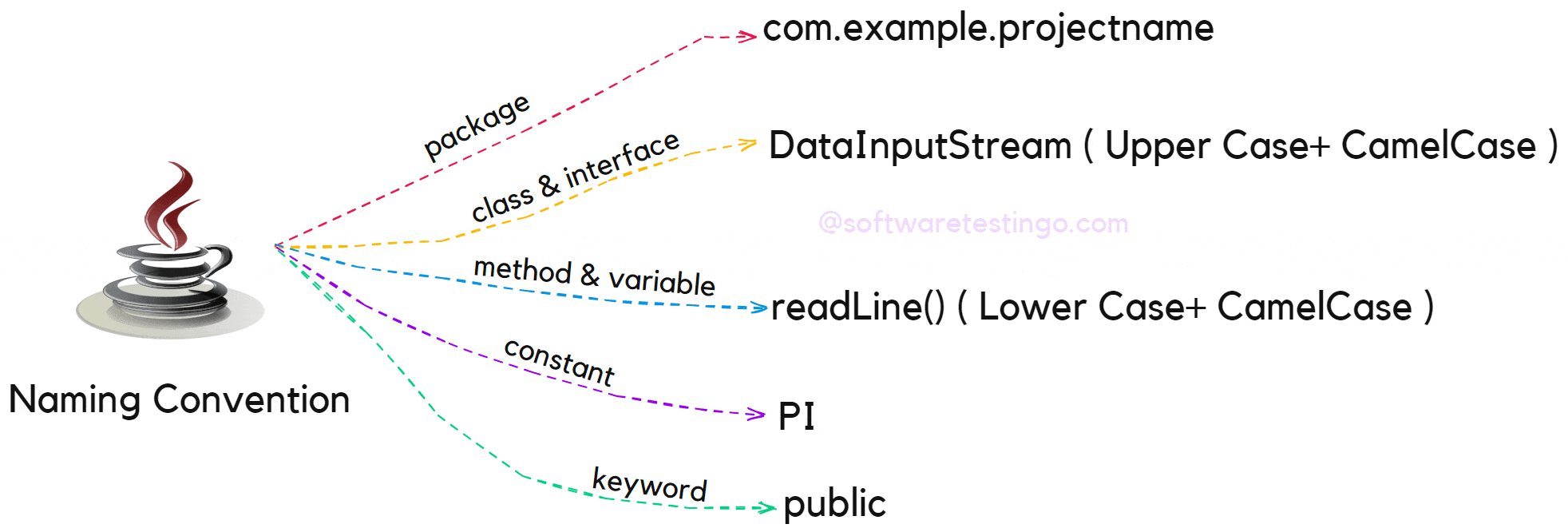
Java Package Naming Convention
In Java, packages are used to organize related classes, and the naming convention for packages is based on the reverse domain name of the company or organization. For example, if the company name is “example.com,” the package name should be “com.example.projectname.” This convention helps avoid naming conflicts between different organizations.
java.awt java.io java.swing
Java Class Naming Convention
In Java, class names should always start with an uppercase letter and follow CamelCase notation. CamelCase notation involves writing compound words in which the first letter of each word is capitalized, and there are no spaces or underscores. For example, the class name “studentInformation” would be written as “StudentInformation” in Java.
String DataInputStream ActionListener
Java Interface Naming Convention
The naming convention for interfaces in Java is similar to classes. The interface’s name should start with an uppercase letter and follow CamelCase notation. In addition, the interface’s name should reflect its purpose, and it’s common to append the suffix “able” or “ible” to indicate that the interface defines a behavior that can be implemented. For example, the interface “Runnable” indicates that the implementing class can be run.
Java Method Naming Convention
In Java, method names should always start with a lowercase letter and follow CamelCase notation. The name should reflect the purpose of the method, and it’s common to use verbs to describe the action performed by the method. For example, a method that adds two numbers could be named “addNumbers.”
printLn() readLine() getName()
Java Variable Naming Conventions
In Java, variable names should start with a lowercase letter and follow CamelCase notation. The name should reflect the purpose of the variable, and it’s common to use nouns to describe the data stored in the variable. For example, a variable that stores a student’s name could be named “studentName.”
age empName dataAddress
Naming Convention For Java Constants
Constants in Java are defined using the “final” keyword, and their names should be written in uppercase letters, separated by underscores. This convention helps distinguish constants from other variables and makes it easier to read code. For example, a constant representing the speed of light could be named “SPEED_OF_LIGHT.”
Naming Convention For Keywords
Firstly, all keywords in Java are lowercase, and it is also recommended that lowercase letters be used.
public void static
By adhering to these conventions, codders can make their code more understandable and easier to maintain and modify, ultimately making it more efficient and effective.
Java Data Types
The data type defines a variable taken as which kind of value it can hold. For example, if you have mentioned a variable with the int data type, that variable can only take integer-type data. Similarly, if you declare a variable with a string, then that variable can take only string-type values.
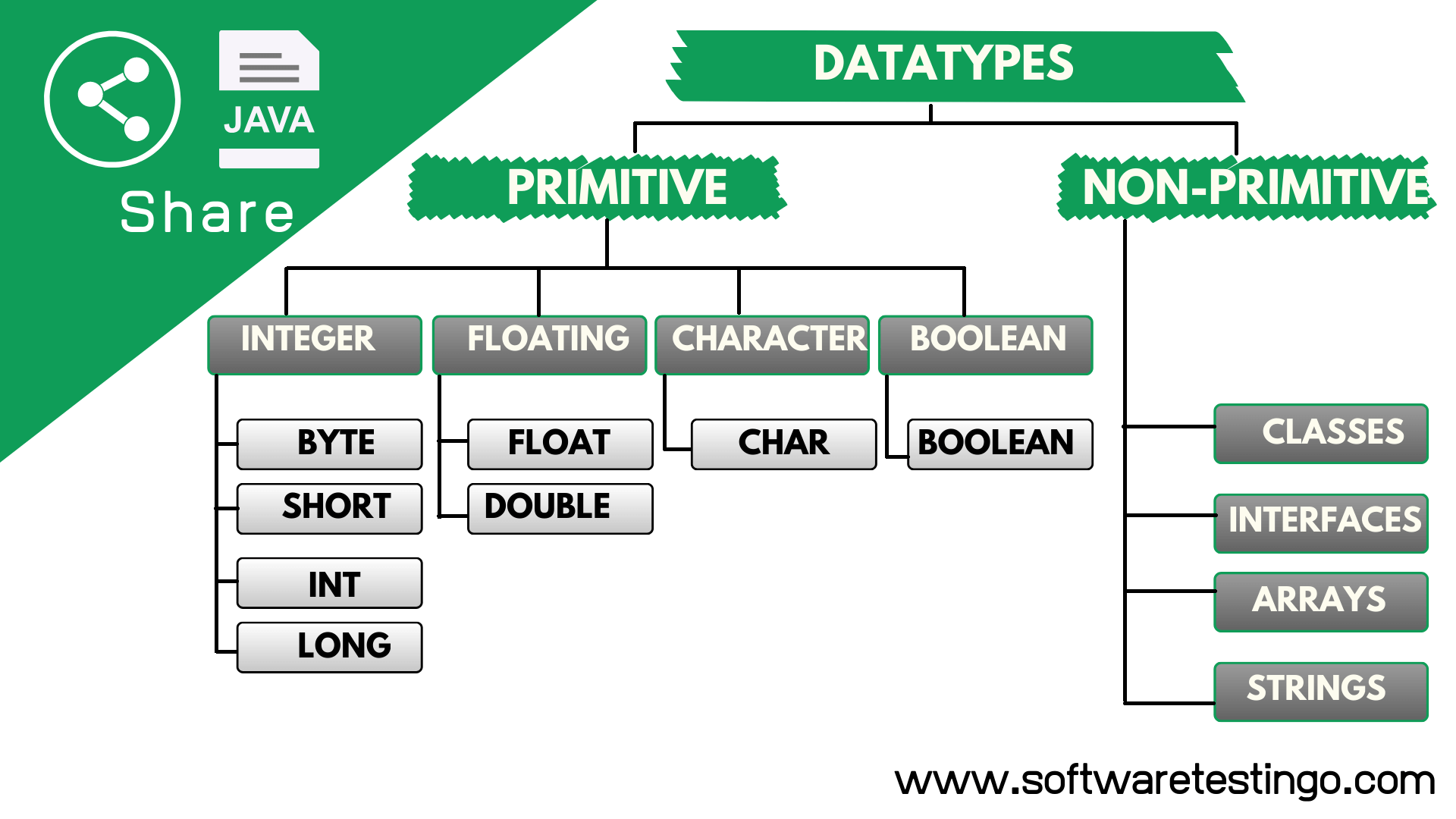
Java is a strongly typed language, meaning each variable must have a declared type, which cannot be changed during runtime. Java has two main categories of data types:
Primitive Data Types in Java
Primitive data types are Java’s most basic Datatypes: byte, short, int, long, float, double, char, and boolean. These data types are not objects and are stored directly in the computer’s memory, making them faster and more memory-efficient than reference types.
In Java, there are eight different primitive data types available that are: Boolean, char, byte, short, int, long, float, and double.
- Where byte, short, int, and long data types are used to store the whole numbers
- Float and double are used for storing fractional numbers
- Char is used for storing characters or letters.
- Boolean is used to store the values like true or false.
Examples of Primitive Data Types in Java
Here is the example with the description of 8 Primitive Data Types in Java:
- Byte: The byte data type stores integers ranging from -128 to 127. For example, byte age = 30;
- Short: The short data type stores integers ranging from -32,768 to 32,767. For example, short price = 1000;
- Int: The int data type stores integers ranging from -2,147,483,648 to 2,147,483,647. For example, int number = 10;
- Long: The long data type stores larger integers ranging from -9,223,372,036,854,775,808 to 9,223,372,036,854,775,807. For example, long largeNumber = 1000000L;
- Float: The float data type stores floating-point numbers with single precision. For example, float pi = 3.14f;
- Double: The double data type stores floating-point numbers with double precision. For example, double price = 12.50;
- Char: The char data type is used to store a single character. For example, char letter = ‘A’;
- Boolean: The boolean data type stores true or false values. For example, boolean flag = true;
Non-primitive Datatypes or Reference Data Types
Non-primitive data Types (Reference Data Types) are more complex and refer to objects created from classes. Reference data types include classes, arrays, and interfaces. Unlike primitive data types, reference types are not stored directly in memory; a reference to the object is stored in memory. This reference points to the object’s location in memory, allowing us to access and manipulate the object’s data.
Examples of Non-Primitive Data Type
Java has four non-primitive data types, and they are:
- Classes: A class is a blueprint for creating objects with similar attributes and behaviors—for example, class Car { String model; int year; double price; }.
- Arrays: An array is a collection of elements of the same data type. Arrays store a fixed number of elements that can be accessed using an index. For example, int[] numbers = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
- Interfaces: An interface is a collection of abstract methods defining a contract for the interface’s classes. For example, interface Drawable { void draw(); }.
- Strings: In Java, a string is an object that represents a sequence of characters, although it is commonly understood as a sequence of characters. The creation of a string object is done using the java.lang.String class. You can read the detailed, informative article on this subject to understand Java Strings further.
Understanding the characteristics of each data type in Java is crucial for designing efficient and effective programs. For instance, using the wrong data type for a particular operation can lead to errors, incorrect results, or even program crashes. Therefore, it’s essential to understand each data type’s size, range of values, and operations that can be performed.
For example, the byte data type stores small integers that require less memory than the int data type, which is used to store larger integers. Similarly, the boolean data type is used to store true or false values, while the char data type is used to store single characters.
Conclusion:
Java has eight primitive data types and four non-primitive data types. Primitive data types are used to store simple values, while non-primitive data types are used to store reference values. Understanding the various data types in Java is essential for any programmer, from beginners to experts. It helps programmers write efficient, robust code that performs the desired operations accurately and quickly.
By choosing the appropriate data type for each variable and operation, we can ensure that our programs run smoothly and are easy to maintain and modify. We hope this detailed explanation article on Java Data types and Naming Conventions will help you write a Java program well and choose the right data type per your requirements.
We believe that feedback is a gift, and we’re always eager to hear what our readers say. If you have any thoughts, opinions, or suggestions, please leave them in the comments section below.
