Abstract Class In Java: An abstract class is a class that cannot be instantiated and serves as a blueprint from which other classes can derive. It is a partially implemented class, where some methods may be left unimplemented or abstract.
An abstract class can have abstract and non-abstract methods, instance variables, and constructors. However, it cannot be instantiated, meaning you cannot create objects of the abstract class. Instead, you must create a subclass that extends the abstract class and implements the abstract methods.
Abstract classes are useful for creating common behaviors and attributes that multiple subclasses can share. They provide a way to define a common interface for a set of related classes while allowing each subclass to implement its own behavior.
Abstraction In Java
Abstraction is the process of hiding the inner implementation details and showing the only functionality to the user. That means what a user wants to see and hiding the inner details of the application or program.
For example, your requirement is to multiply two numbers using the calculator. For that, you press two numbers with multiple symbols in the calculator, and finally, you get the result, but you don’t know the internal multiplication process.
How to Achieve Abstraction?
We can achieve abstraction in two ways:
- Using an abstract class
- By Implementing Interface
Abstract Class in Java
In this article, we are going to discuss:
- What is an abstract class?
- Why do We need an abstract class?
- How to Declare an abstract class?
- Why Can’t We create an object of an abstract class?
- Important points to remember about Abstract class
What is an abstract class?
The class declared with the keyword “abstract” is called an abstract class. An abstract class contains a concrete method (method with the body) and an abstract method (method without the body). In Java programming language, normal classes have concrete methods but no abstract methods.
Why do We Need an abstract class?
An abstract class is helpful when we have the required details, but it’s incomplete, and we don’t know the full implementation at that time. It is useful to define that class as an abstract class by declaring that as an abstract class, we force the user to implement later when the user has the complete implementation details. If the user has not implemented the abstract methods, he will get a compilation error.
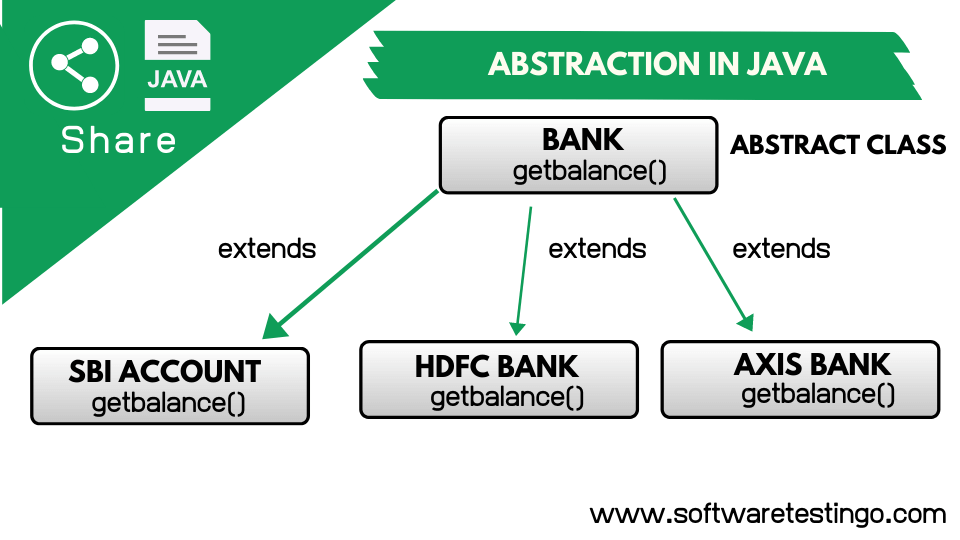
Let’s take an example of a Bank Application. As per the government rules, every bank has some basic features like deposit, Withdrawal, etc., but when it comes to the bank level, every bank has a different implementation process. So, in that case, the Government bodies can declare a class “Features” and make that abstract, so when it comes to the bank level, they have to implement the abstract methods declared by the Government bodies.
package com.softwaretestingo.abstraction;
//abstract parent class
abstract class Rbi
{
//abstract method
public abstract void deposit();
}
public class BankChildex extends Rbi
{
public void deposit()
{
System.out.println("Deposit Method Of BankChildex Class executed");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
// Child Class Method Will Be Called
Rbi obj=new BankChildex();
obj.deposit();
}
}
How to Declare an Abstract Class?
We can declare an abstract class below, with abstract and concrete methods.
//Declaration using abstract keyword
abstract class A
{
//This is an abstract method
abstract void myMethod();
//This is a concrete method with body
void anotherMethod()
{
//Does something
}
}
Rules:
- In many cases, it is difficult or unnecessary to implement all the methods without complete information in the parent class. In those cases, we can declare the parent class as an abstract class so that whichever class extends the parent class, the class must need to implement the unimplemented or abstract methods of the parent class.
- If the child class has not implemented the abstract methods of the parent class, then the child class needs to be declared as abstract.
- An abstract class can not be instantiated, which means you can not create an object of an abstract class. To use an abstract class, you must create another class that extends an abstract class and implements all the abstract methods. After implementation, you can create an object of the child class to call the abstract methods or parent class and implement methods of the child class.
Why can’t you create the object of the abstract class?
Abstract classes are not complete because they have incomplete methods (abstract methods) with no method body. What will happen if you can create an object and call an abstract method in Java programming language because those methods don’t have any implementation? The other thing is an object, which is concrete, but an abstract class is a template. So, to create an object, you have to extend an abstract class and build a completely implemented class; after that, you can create the object.
Let’s take an example for understanding.
package com.softwaretestingo.abstraction;
abstract class AbstractDemo
{
//Concrete Method
public void myMethod()
{
System.out.println("Hello");
}
//Abstract Method
abstract public void anotherMethod();
}
public class AbstractChildDemoEx
{
public void anotherMethod()
{
System.out.println("Child Class anotherMethod Executed");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//error: You can't create an object of it
AbstractDemo obj = new AbstractDemo();
obj.anotherMethod();
}
}
Abstract class in Java Important Points
- The abstract keyword is used to create an abstract class.
- You can’t instantiate an abstract class.
- To create an abstract method, we need to use the keyword “abstract,” and abstract methods don’t have a method body.
- If a class has abstract methods, then that class must be declared with an abstract keyword.
- An abstract class doesn’t need an abstract method; we can make an abstract class even if we don’t have any abstract methods.
- If an abstract class has no method implementation, it’s better to declare it as an interface Because Java programming language doesn’t support multiple inheritances.
- If a class extends an abstract class, that extended class should have implemented all the abstract methods; otherwise, the extended class should be declared with the “abstract” keyword.
- In an abstract class, we can implement an interface without implementing any methods of an interface.
- With the help of the abstract class, we can provide a common method implementation to all the subclasses.
Ref: article
Can abstract classes have method implementation?
Yes, since an abstract class can contain both abstract and non-abstract methods.
What is an Abstract Class in Java?
An abstract class is a class that may or may not contain some abstract methods. It cannot be instantiated. A Java Abstract class provides a common method implementation to all its extended subclasses.
What is the difference between abstract methods and concrete methods?
Abstract methods do not have a method body, while concrete methods do.
What is an Abstract Method in Java?
It is a method that does not have any definition. It is the responsibility of the subclass methods to implement such methods concretely. In doing so, each subclass is free to give its own implementation of the abstract method.
Why are there no abstract constructors?
The abstract constructor will never get invoked in such a case, as the subclasses cannot inherit constructors. That is why we don’t have abstract constructors in Java.
What is the difference between abstract class and interface?
The main difference is that abstract classes can contain abstract and concrete methods, while interfaces support only abstract methods.
Where do we use an abstract class?
An abstract class defines a base class, which the derived class can later override.
