Method In Java: In Java, a method is a block of code that performs a specific task or set of tasks. Methods are an essential part of Java programming, as they allow you to organize and modularize your code, making it more readable, reusable, and maintainable.
Java is an object-oriented programming language with classes like Python and . NET. We can declare variables, methods, constructors, and blocks inside a class. These are the elements that a class can contain.
In our previous blog post, we discussed variables in detail and the three types of variables: local, instance, and static variables. This blog post will discuss the importance of methods in a class and how to use them in your Java Programs.
The purpose of methods is to write the logic of your application. Inside a class, you cannot write logic directly. That’s why we declare methods within a class. So, methods are used to encapsulate and organize the logic of your program.
Method In Java Definition or What Is A Method In Java?
In Java, a method is a self-contained block of code within a class that defines a specific behavior or operation. or we can say Methods encapsulate functionality and can be called or invoked to perform tasks within a Java program.
Methods are fundamental building blocks of object-oriented programming in Java and serve various purposes, including data manipulation, calculations, and interaction with objects. Also, Java Methods helps achieve abstraction, reusability, and modularization.
Type Of Method In Java
In Java, we have two types of methods based on their creation or availability. The methods in Java are categorized according to attributes like: Does a user define the method, or is the method available in the standard library?
Based on that, methods divided into two types, that is:
Standard Library Method In Java
The Standard Library Methods methods are nothing but the built-in methods, which are already available inside the Java standard libraries, which come with the Java Class Library (JCL) in a Java archive (*.jar) file with JVM and JRE.
Some Examples of Standard Library Methods are:
- Print(): This method is available inside the java.io.PrintSteam package. This print(“….”) method prints in the console. Whatever you will write inside the quotation marks will print inside the console.
- Sqrt (): This method belongs to the math class. It will return the square root of the given number.
User-Defined Method In Java
A user-defined method in Java is a method that the programmer creates to perform a specific task within a Java program. Unlike built-in methods already included in Java, user-defined methods are created by the programmer and tailored to the program’s specific needs.
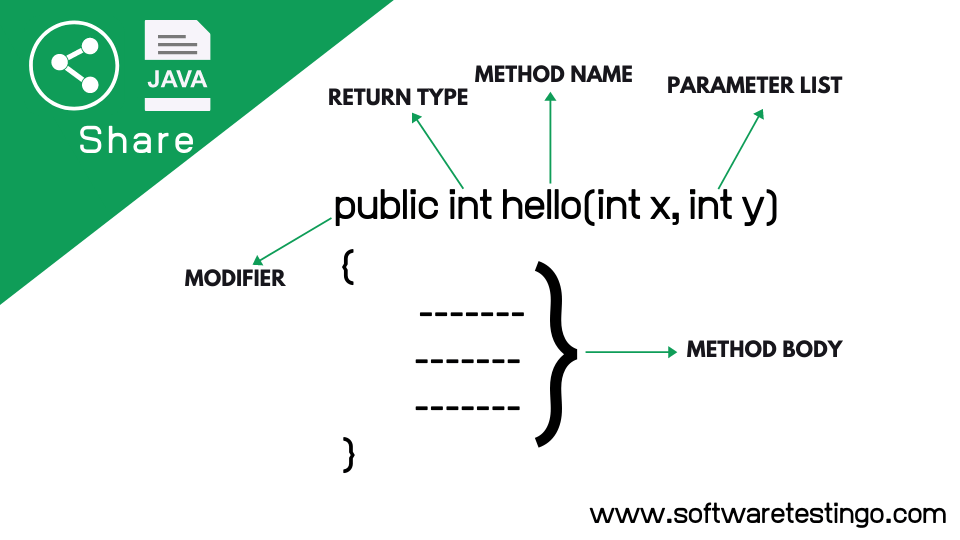
Syntax of Method
To Declare or create a method in Java, you can follow the syntax:
<access_modifier> <return_type> <method_name>( list_of_parameters)
{
//body
}
Method Declaration
Key components of a method in Java include:
- Method Name: A method is identified by its name and also used to call or invoke the method.
- Return Type: Methods can optionally return a value after their execution. The return type specifies the data type of the value returned, and if a method doesn’t return anything, its return type is declared void.
- Parameters: Methods may accept input values, known as parameters or arguments. Parameters are enclosed in parentheses after the method name, allowing you to pass data to the method for processing.
- Method Body: The method body is enclosed in curly braces { } and contains the code that defines the method’s behavior. This code is executed when the method is called.
- Access Modifiers: Access modifiers such as public, private, protected, or package-private determine the visibility and accessibility of the method from other classes and packages.
We have discussed various Java Access modifiers in a separate post in detail, and you can check that by following the link.
From the above image, you can notice we have the following:
- public static − modifier
- int − return type
- methodName − the name of the method
- a, b − formal parameters
- int a, int b − list of parameters
How to Name a Method ( Method Naming Convention )
The method name is always a single word; sometimes, the name begins with a lowercase verb followed by an adjective or noun. There is a naming convention for methods like after the first-word first letter of words should be in the capital letter. For Example softwareTestingo, findElement
Note: The method must have a unique name within the class, but sometimes a class can have multiple methods with the same name but different parameters, called method overloading.
How to Call Java Method
Suppose you have defined a method, and later, you want to use that method. So, to use that method, you need to call that method. Let’s understand how to call a method.
myMethod();
This statement is called myMethod(), which was declared earlier.
- While Java executes the program code, it encounters myMethod(); in the code.
- The execution then branches to the myFunction() method and executes code inside the method’s body.
- After the execution of the code inside the method body, the program returns to the original state and executes the next statement.
Java Method Example
package java_Basics;
public class Method_Example
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Going to Call static method myMethod()");
// method call
myMethod();
System.out.println("myMethod was executed successfully!");
}
// method definition
private static void myMethod(){
System.out.println("Printing from inside myMethod()!");
}
}
Various Other Method Types in Java
But if we are looking based on the purpose and functionality, we can find several types of methods in Java. Here we tried to list some of the most common types of methods in Java are:
Instance Methods: These are the most common types of methods in Java and are associated with an instance of a class. They are used to access and modify instance variables and perform specific tasks related to the object. Instance methods are defined without the static keyword and can access non-static variables and methods.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
class Class_Rectangle
{
private int length;
private int width;
public void setDimensions(int len, int wid)
{
length = len;
width = wid;
}
public void getArea()
{
int area=length * width;
System.out.println("The Area is: "+area);
}
}
public class InstanceMethodEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Class_Rectangle obj=new Class_Rectangle();
obj.setDimensions(10, 20);
obj.getArea();
}
}
Static Methods: These methods are associated with a class rather than an instance of a class. They are used to perform tasks that do not require access to instance variables or methods. Static methods are defined using the static keyword and can only access static variables and methods.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
public class StaticMethodEx
{
//Static Variable
static int a=10;
//Static Method
static void display()
{
System.out.println("The Static Value Of a Is: "+a);
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
display();
}
}
Constructors: Constructors are special methods used to initialize objects when they are created. They have the same name as the class and do not have a return type. Constructors can be overloaded, allowing a class of multiple constructors with different parameters.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
class cEx
{
String name;
int id;
public cEx(String name, int id)
{
this.name=name;
this.id=id;
}
}
public class ConstructMethodEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
cEx obj=new cEx("SoftwareTestingo", 5);
System.out.println("Name :" + obj.name + " and Id :" + obj.id);
}
}
Getter and Setter Methods: Getter methods are used to retrieve the value of an instance variable, while setter methods are used to set or modify the value of an instance variable. These methods are often used to ensure encapsulation and data hiding in object-oriented programming.
These two getters and setter methods are two different types of Instance methods.
The accessor method (Getters), also known as a getter, enhances the code’s security and protection level. This method returns the value of a specific data type, such as int, String, double, float, etc., to allow access to the data. To facilitate the program’s implementation, the getter usually begins with the word “get” followed by the variable name.
The mutator method (Setters) sets the value of variables used in a class’s programs. This method typically begins with the word “set” followed by the variable name. Both the getter and setter methods facilitate the programmer in setting and retrieving the value of a particular data type. It is recommended that the first letter of the variable name be capitalized in both the getter and setter methods.
Accessor and mutator are mainly used to access or set the value for the private member of the class in the main method.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
class accessormutator
{
//private variable
private int value=10;
// Mutator method (setter)
public void setValue(int a)
{
// return balance + a;
value=value+a;
}
// accessor method (getter)
public int getValue()
{
return value;
}
}
public class GettersSettersEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
accessormutator obj=new accessormutator();
//setting new value
obj.setValue(30);
System.out.println("Your Value : "+obj.getValue());
}
}
Void Methods: Void methods do not return any value and are used to perform a specific task without returning a result.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
public class VoidMethodEx
{
public static void displayValue()
{
System.out.println("displayValue void method called");
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
displayValue();
}
}
Return Methods: Return methods are used to perform a specific task and return a value. The return type is specified in the method signature, and the method must return a value of that type.
Abstract Methods: Abstract methods are defined in abstract classes and do not have a method body. They are used to define a method signature that any subclass of the abstract class must implement.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
abstract class operations
{
abstract public void printinfo();
}
class addition extends operations
{
public void printinfo()
{
int a=110;
int b=20;
System.out.println("The Sum Of Values : "+(a+b));
}
}
class subsctraction extends operations
{
public void printinfo()
{
int a=110;
int b=20;
System.out.println("The Substraction Of Values : "+(a-b));
}
}
public class Arithmatic_OperationEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
operations obj=new addition();
obj.printinfo();
operations obj1=new subsctraction();
obj1.printinfo();
}
}
Final Methods: Final methods cannot be overridden by subclasses and are used to ensure that a method’s implementation cannot be changed.
package com.softwaretestingo.Basic;
class Show
{
//final method
public final void show()
{
System.out.println("Inside final method");
}
}
class FinalMethodTest extends Show
{
//try to override final method
public void show()
{
System.out.println("Inside overridden final method");
}
}
public class FinalMethodEx
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
//creating object of FinalMethodTest Class
FinalMethodTest obj = new FinalMethodTest();
//method call
obj.show();
}
}
In Java, you can not override the final method; if you try to do so, then you will get the below exception:
Exception in thread "main" java.lang.IncompatibleClassChangeError: class com.softwaretestingo.Basic.FinalMethodTest overrides final method com.softwaretestingo.Basic.Show.show()
Native Methods: Native methods are written in a language other than Java and are used to access system resources or perform tasks that are not possible in Java.
Understanding the different types of methods in Java is essential for writing efficient and effective code. Each type of method has its specific purpose and functionality and can be used to perform specific tasks in a Java program.
Please write comments if you find anything incorrect or if you want to share more information about the above-discussed topic.
What are methods in Java?
A method in Java is a set of instructions that can be called for execution using the method name. A Java method can take in data or parameters and return a value – both parameters and return values are optional. Methods can be public, private or protected.
How many types of methods are there in Java?
In Java, we have 2 types of methods: Standard Library Methods & User-Defined methods.
What is the method type in Java?
A method is a collection of statements that perform some specific task and return the result to the caller. A method can perform some specific task without returning anything. Methods allow us to reuse the code without retyping the code.
What is a static method in Java?
Static Method in Java belongs to the class and not its instances. A static method can access only static variables of the class and invoke only static methods of the class.
