Our previous posts taught us about OOPS concepts, Java string, and other core Java tutorials. Now, let’s start learning some of the advanced concepts of Java programming language, i.e., Java Collection Framework.
the Java programming language supports Arrays to store several objects in it, but when we have initialized an array with a predefined size during instantiation. We Can store groups of objects in an array and also retrieve them easily, but there are some inconveniences:
- We can not store different class objects in the same array. The reason is an array can store only one data type of elements.
- Adding the objects at the end of an array is easy, but inserting and deleting the elements in the middle of an array is difficult. In that case, we have to rearrange the elements of the array.
- Retrieving elements from an array is easy, but no methods are available to process them.
Due to the above problems, programmers want a better mechanism to store a group of objects. The alternative way is using an object to store a group of other objects. That means we can use a class object as an array; such an object is called a “collection object” or “container object”, and for more flexible data structures, the core Java library provides the collection framework.
What is a Java Collection Framework?
A Java collection framework provides an architecture to store and manipulate a group of objects. A Java collection framework has the following things in it:
- Interfaces
- Classes
- Algorithm
Interfaces: Interfaces provide an abstract data type to represent the collection and java.util.collection is the root interface of the collection framework. and the collection interface also contains some methods like size(), iterator(), add(), remove(), and clear(), etc, so every collection class should implement those methods as well as some interfaces like java.util.List, java.util.Set, java.util.Queue and java.util.Map.
The map is the only interface not inherited from the collection interface but is part of the collection framework. All the collection framework interfaces are inside Java.util package.
Implemented Classes: Collections in Java provide the implementation of the collection interface. Some important classes are ArrayList, LinkedList, HashMap, TreeMap, HashSet, and TreeSet. These classes help solve most of our programming needs, but if we need more unique features, we must extend them and create our custom collection class. All the collection classes are present inside java.util package.
Algorithm: It refers to the methods that we use to perform the operations like sorting and searching on the objects that implement the collection interface.
Benefits of Java Collection Framework
Here are the benefits of the Java collection framework:
- Reduced Development Effort: As it has all common collections and useful methods that help iterate and manipulate the data, we can concentrate more on developing the business logic than designing collection API.
- Increased Quality: The Collection classes are well tested, so it helps to increase our program quality rather than using a developed data structure.
Java Collection Framework Hierarchy
As we have learned, the Java collection framework has combinations of Interfaces and classes. Let’s understand that collection framework hierarchy to understand the framework better.
Java Collections Interfaces
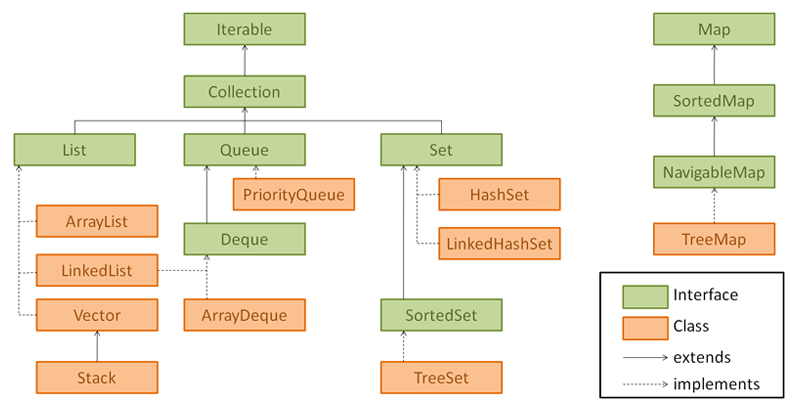
As we saw in the above picture, the collection framework combines classes and interfaces. The total framework collection interface is the root interface for the Java collection framework, and the collection interface is generic.
For example, public interface Collection<E>.
When we declare a collection interface, we need to specify the type of object it can contain so we can mention <E> in the above syntax, and the <E> syntax is for Generics.
The Java Collections framework contains the below interfaces:
Collection Interface
The root interface for the Java collection framework is a collection interface. A collection represents a group of objects known as its elements. The Java programming language doesn’t provide any direct implementation of this interface.
The Interface has different methods in it, those are:
- Size()
- isEmpty()
- contains() – To Check whether the object is present in the collection or not
- add() and remove() – to add or remove an element from the collection
- iterator() – it helps to iterate elements of the collection
The collection interface also has some bulk operations methods which work over the entire collection. Those methods are:- containsAll, addAll, removeAll, retainAll, clear.
Another method is present in the collection interface, toArray(); this method acts as a bridge between collections and Older API, which expects arrays on Input.
Important Points about the Collection Interface
- If we want to represent a group of individual objects as a single entity, we should go for the collection.
- The collection interface defines the most common methods for any collection object.
- In the general collection, the interface is considered the root interface of the collection framework.
- No concentrate class implements the collection interface directly.
Difference between Collection & Collections
| Collection | Collections |
|---|---|
| The collection is an interface | Collections is a utility class. |
| It is used to represent a group of individual objects as a single unit. | It defines several utility methods that are used to operate on collection. |
| The Collection is an interface that contains a static method since java 8. The Interface can also contain abstract and default methods.. | It contains only static methods. |
| It extends the iterable interface. | It extends the Object class. |
| Basic collection interface implementations do not inherently support thread-safety. | Collections class provides methods to make specific collections thread-safety. |
List Interface
- It is the child interface of the collection.
- If we want to represent a group of individual objects as a single entity where duplicates are allowed and insertion order must be preserved, then we should go for the List.
- You can access the elements using the index, and the size of a List interface is dynamic.
- The implementation classes of the List interface are ArrayList and LinkedList.
Set Interface
- It is the child interface of the collection.
- If we want to represent a group of individual objects as a single entity where duplicates are not allowed and insertion order is not preserved, then we should go for the Set.
- The size of the Set will increase dynamically when you add elements to it.
- A Set will not allow duplicate elements; if you try inserting them, it is not stored in the set.
- In Java, the Set interface has three implementation classes: HashSet, TreeSet, and LinkedHashSet.
- The set interface doesn’t allow random access to elements in the collection, but you can use an iterator or for-each loop for traversing the elements of a Set Interface.
SortedSet Interface
- SortedSet Interface is a child interface of Set Interface.
- Suppose we want to represent a group of individual objects as a single entity where duplicates are not allowed, and all objects should be inserted according to some sorting order. In that case, we should go for the sorted set.
NavigableSet Interface
- It is the child interface of the sorted set.
- It contains several methods for navigation purposes.
Queue Interface
- It is the child interface of the collection.
- If we want to represent a group of individual objects prior to processing, we should go for the queue.
- Usually, the queue follows the First In, First Out (FIFO) order, which means the element that is stored as the first element in the queue will be removed first from the queue. But based on our requirements, we can also implement our priority order.
Dequeue Interface
This Collection interface supports the element insertion and deletion at both ends. This interface has methods like insert(), remove(), and examine the element.
Map Interface
- The map is not a child interface of the Collection interface.
- If we want to represent a group of objects as key-value pairs, we should go for the map if Both key-value values are objected to only.
- If the key value is provided, then we can retrieve the corresponding value. But the key value should be unique.
- Duplicate keys are not allowed, but values can be duplicated.
- Map interface has three implementation classes: HashMap, TreeMap, and LinkedHashMap.
- The basic operations we do with Map are put, get, containsKey, value, size, and isEmpty.
SortedMap Interface
- It is the child interface of Map.
- If we want to represent a group of objects as key-value pairs and store them according to some sorting order of keys, we should go for the sorted map.
- In a sorted map, the sorting should be based on the key, not values.
Navigable Map Interface
- It is the child interface of the sorted map.
- It defines several methods for navigation purposes.
Note:
- Usually, we can use the collection to hold and transfer objects from one location to another.
- Every collection class implements a serializable and cloneable interface to support this requirement by default.
- Whereas ArrayList and vector classes implement a random access interface, when we are trying to access any random element from ArrayList and Vector, we can access it with the same speed.
Random access Interface
- Random access interface is present in Java.util package and contains no methods.
- It is a marker interface, so JVM will automatically provide the required ability whenever needed.
- ArrayList is the best choice if your frequent operation is a retrieval operation. (Because ArrayList implements a random access interface)
- ArrayList is not the correct choice if our frequent operation inserts and deletes the element in the middle.
Iterator Interface
This interface provides methods by which we can iterate collection elements. For that, we need to create an Iterator instance, and we can iterate the collection elements. Also, using an iterator, you can remove the elements from the collection.
ListIterator Interface
ListIterator is an interface that contains a method to retrieve the elements from the collection object, both in a forward and reverse direction. It have following methods: hasNext(), hasPrevious(), next(), previous() and remove().
SortedMap Interface
It’s a child interface of the Map interface. In this interface, the keys are stored in ascending order.
Java Collections Classes
The Java Collection framework has many implementation classes for different interfaces. The common implementation classes of these are ArrayList, HashMap, and HashSet. The collection classes are not thread-safe, and their iterator also fails fast. Below, we are trying to share some of the commonly used implementation classes:
HashSet Class
Java HashSet is the basic implementation class of the Set interface. It does not guarantee the order of the elements. Duplicate elements cannot be stored, and you can insert null values.
These classes have methods like add, remove, contain, and size. We can also see this implementation class’s initial capacity and load factor—the load factor measures how full the hash map can get before its capacity is automatically increased.
TreeSet Class
Java TreeSet class implements the set Interface, which uses a tree for storage. This TreeSet class inherits the abstract and implements the NavigableSet Interface. In the Tree set, the elements are stored in ascending order, and duplicated elements are not allowed.
ArrayList Class
Java ArrayList class inherits an abstract class and implements the list interface, and this class uses a dynamic array to store the elements. This is used to store similar elements. As for a standard Array, we need to declare the size of the array before we use it, and once the size is declared, it’s fixed, but in the case of ArrayList, we do not need to declare the size its grow as we are adding the elements into it.
LinkedList Class
The Java LinkedList Class used a double-linked list to store the elements. Here, the elements are stored as data and address parts, each known as a node. Due to the ease of insertion and deletion, LinkedList is preferred over arrays. The LinkedList class implements the list interface.
HashMap Class
The HashMap Class used a hashtable and implemented the map interface. You can do all map operations, and it also permits null values and null keys. This HashMap Class is almost equivalent to Hashtable, except it is synchronized and also permits null\.
TreeMap Class
TreeMap class implements the Map interface. It also extends the abstract map and implements the NavigableMap interface. This TreeMap class is a red-black tree-based implementation. You can store the key-value pairs in sorting order.
PriorityQueue Class
As we have discussed above, the elements of the queues are in FIFO order, but sometimes, we want to process the elements in priority order. In that case, the priority queue helps to process the elements, and the priority queue does not allow null values.
Collections class
The collection class implements the collection interface, which is defined inside the java. util package. In this class, some of the classes provide full implementations, which can be used as they are, and some of them are abstract, which need to be fully implemented to create concentrated collections.
This class contains methods for collection framework such as binary search, sorting, shuffling, reverse, etc.
Collections API Algorithms
The collection framework also provides some of the implementations of commonly used algorithms, like Sorting and searching. Most methods have algorithm implementations that work on the list; some are for collections.
Sorting
By using these algorithms, users can sort the elements in ascending order. There are two forms of this operation: making a list and sorting its elements in ascending order of elements with natural ordering. The second form is sorting the elements with the help of a comparator.
Shuffling
This helps in destroying the sorting order if the list elements are in any order. This algorithm helps in implementing games.
Searching
This search algorithm helps find the specified elements in a sorted list. This algorithm also has two forms where it takes a list and the search element, but it assumes the list elements are in sorted order. The second form is taking a comparator with the list and search item, assuming the list is sorted into ascending order according to the specified comparator. Here, the sort algorithms are called first to sort the elements before calling binary search.
Min and Max values
These two algorithms find the maximum and minimum elements of the collection. This algorithm also comes in two forms. the first takes a natural ordering of elements and returns the maximum or minimum elements from the collection, and the second form takes a comparator with the collection and returns the maximum or minimum elements according to the specified comparator.
